Thesis High-Resolution Photoemission Study of Kondo Insulators ...
Thesis High-Resolution Photoemission Study of Kondo Insulators ...
Thesis High-Resolution Photoemission Study of Kondo Insulators ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
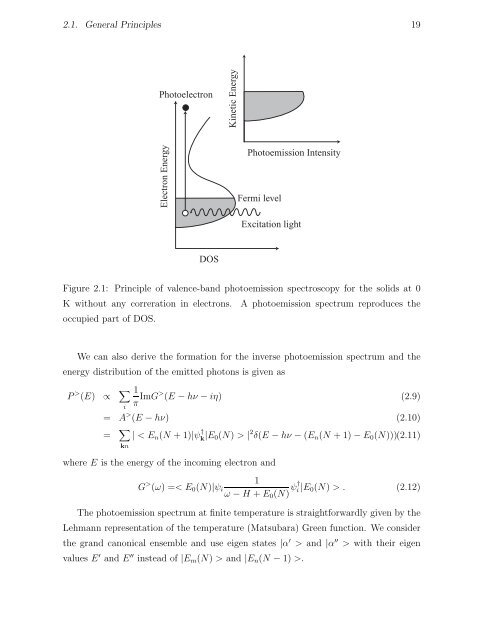
2.1. General Principles 19<br />
Photoelectron<br />
Electron Energy<br />
DOS<br />
Kinetic Energy<br />
<strong>Photoemission</strong> Intensity<br />
Fermi level<br />
Excitation light<br />
Figure 2.1: Principle <strong>of</strong> valence-band photoemission spectroscopy for the solids at 0<br />
K without any correration in electrons. A photoemission spectrum reproduces the<br />
occupied part <strong>of</strong> DOS.<br />
We can also derive the formation for the inverse photoemission spectrum and the<br />
energy distribution <strong>of</strong> the emitted photons is given as<br />
P > (E) ∝ � 1<br />
i π ImG> (E − hν − iη) (2.9)<br />
= A > (E − hν) (2.10)<br />
= �<br />
kn<br />
| | 2 δ(E − hν − (En(N +1)− E0(N)))(2.11)<br />
where E is the energy <strong>of</strong> the incoming electron and<br />
G > 1<br />
(ω) =. (2.12)<br />
The photoemission spectrum at finite temperature is straightforwardly given by the<br />
Lehmann representation <strong>of</strong> the temperature (Matsubara) Green function. We consider<br />
the grand canonical ensemble and use eigen states |α ′ > and |α ′′ > with their eigen<br />
values E ′ and E ′′ instead <strong>of</strong> |Em(N) > and |En(N − 1) >.