Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
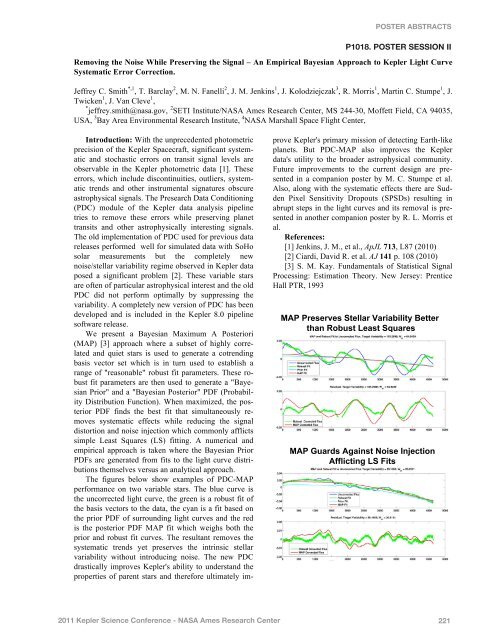
POSTER ABSTRACTSP1018. POSTER SESSION IIRemoving the Noise While Preserving the Signal – An Empirical Bayesian Approach to <strong>Kepler</strong> Light CurveSystematic Error Correction.Jeffrey C. Smith *,1 , T. Barclay 2 , M. N. Fanelli 2 , J. M. Jenkins 1 , J. Kolodziejczak 3 , R. Morris 1 , Martin C. Stumpe 1 , J.Twicken 1 , J. Van Cleve 1 ,* jeffrey.smith@nasa.gov, 2 SETI Institute/<strong>NASA</strong> Ames Research Center, MS 244-30, Moffett Field, CA 94035,USA, 3 Bay Area Environmental Research Institute, 4 <strong>NASA</strong> Marshall Space Flight Center,Introduction: With the unprecedented photometricprecision of the <strong>Kepler</strong> Spacecraft, significant systematicand stochastic errors on transit signal levels areobservable in the <strong>Kepler</strong> photometric data [1]. Theseerrors, which include discontinuities, outliers, systematictrends and other instrumental signatures obscureastrophysical signals. The Presearch Data Conditioning(PDC) module of the <strong>Kepler</strong> data analysis pipelinetries to remove these errors while preserving planettransits and other astrophysically interesting signals.The old implementation of PDC used for previous datareleases performed well for simulated data with SoHosolar measurements but the completely newnoise/stellar variability regime observed in <strong>Kepler</strong> dataposed a significant problem [2]. These variable starsare often of particular astrophysical interest and the oldPDC did not perform optimally by suppressing thevariability. A completely new version of PDC has beendeveloped and is included in the <strong>Kepler</strong> 8.0 pipelinesoftware release.We present a Bayesian Maximum A <strong>Poster</strong>iori(MAP) [3] approach where a subset of highly correlatedand quiet stars is used to generate a cotrendingbasis vector set which is in turn used to establish arange of "reasonable" robust fit parameters. These robustfit parameters are then used to generate a "BayesianPrior" and a "Bayesian <strong>Poster</strong>ior" PDF (ProbabilityDistribution Function). When maximized, the posteriorPDF finds the best fit that simultaneously removessystematic effects while reducing the signaldistortion and noise injection which commonly afflictssimple Least Squares (LS) fitting. A numerical andempirical approach is taken where the Bayesian PriorPDFs are generated from fits to the light curve distributionsthemselves versus an analytical approach.The figures below show examples of PDC-MAPperformance on two variable stars. The blue curve isthe uncorrected light curve, the green is a robust fit ofthe basis vectors to the data, the cyan is a fit based onthe prior PDF of surrounding light curves and the redis the posterior PDF MAP fit which weighs both theprior and robust fit curves. The resultant removes thesystematic trends yet preserves the intrinsic stellarvariability without introducing noise. The new PDCdrastically improves <strong>Kepler</strong>'s ability to understand theproperties of parent stars and therefore ultimately improve<strong>Kepler</strong>'s primary mission of detecting Earth-likeplanets. But PDC-MAP also improves the <strong>Kepler</strong>data's utility to the broader astrophysical community.Future improvements to the current design are presentedin a companion poster by M. C. Stumpe et al.Also, along with the systematic effects there are SuddenPixel Sensitivity Dropouts (SPSDs) resulting inabrupt steps in the light curves and its removal is presentedin another companion poster by R. L. Morris etal.References:[1] Jenkins, J. M., et al., ApJL 713, L87 (2010)[2] Ciardi, David R. et al. AJ 141 p. 108 (2010)[3] S. M. Kay. Fundamentals of Statistical SignalProcessing: Estimation Theory. New Jersey: PrenticeHall PTR, 1993!"#$#%&'&%(&'$)*&++,%$-,%.,/.+.*0$1&**&%$*2,3$45/6'*$7&,'*$)86,%&'!"#$%&'()*$"+',-*.$/0,*1$2-314.,0-"556,4.,-+$78$9,.*2011 <strong>Kepler</strong> Science Conference - <strong>NASA</strong> Ames Research Center 221