Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
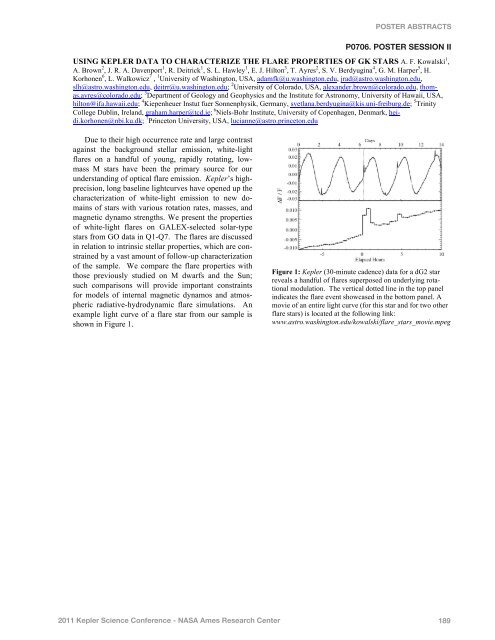
POSTER ABSTRACTSP0706. POSTER SESSION IIUSING KEPLER DATA TO CHARACTERIZE THE FLARE PROPERTIES OF GK STARS A. F. Kowalski 1 ,A. Brown 2 , J. R. A. Davenport 1 , R. Deitrick 1 , S. L. Hawley 1 , E. J. Hilton 3 , T. Ayres 2 , S. V. Berdyugina 4 , G. M. Harper 5 , H.Korhonen 6 , L. Walkowicz 7 , 1 University of Washington, USA, adamfk@u.washington.edu, jrad@astro.washington.edu,slh@astro.washington.edu, deitrr@u.washington.edu; 2 University of Colorado, USA, alexander.brown@colorado.edu, thomas.ayres@colorado.edu;3 Department of Geology and Geophysics and the Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii, USA,hilton@ifa.hawaii.edu; 4 Kiepenheuer Instut fuer Sonnenphysik, Germany, svetlana.berdyugina@kis.uni-freiburg.de; 5 TrinityCollege Dublin, Ireland, graham.harper@tcd.ie; 6 Niels-Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Denmark, heidi.korhonen@nbi.ku.dk;7 Princeton University, USA, lucianne@astro.princeton.eduDue to their high occurrence rate and large contrastagainst the background stellar emission, white-lightflares on a handful of young, rapidly rotating, lowmassM stars have been the primary source for ourunderstanding of optical flare emission. <strong>Kepler</strong>’s highprecision,long baseline lightcurves have opened up thecharacterization of white-light emission to new domainsof stars with various rotation rates, masses, andmagnetic dynamo strengths. We present the propertiesof white-light flares on GALEX-selected solar-typestars from GO data in Q1-Q7. The flares are discussedin relation to intrinsic stellar properties, which are constrainedby a vast amount of follow-up characterizationof the sample. We compare the flare properties withthose previously studied on M dwarfs and the Sun;such comparisons will provide important constraintsfor models of internal magnetic dynamos and atmosphericradiative-hydrodynamic flare simulations. Anexample light curve of a flare star from our sample isshown in Figure 1.Figure 1: <strong>Kepler</strong> (30-minute cadence) data for a dG2 starreveals a handful of flares superposed on underlying rotationalmodulation. The vertical dotted line in the top panelindicates the flare event showcased in the bottom panel. Amovie of an entire light curve (for this star and for two otherflare stars) is located at the following link:www.astro.washington.edu/kowalski/flare_stars_movie.mpegReferences: Use the brief numbered style commonin many abstracts, e.g., [1], [2], etc. References shouldthen appear in numerical order in the reference list, andshould use the following abbreviated style:[1] Author A. B. and Author C. D. (1997) Nat., 90,1151–1154. [2] Author E. F. et al. (1997) ApJ, 32,A74. [3] Author G. H. (1996) LPS XXVII, 1344–1345.[4] Author I. J. (2002) LPS XXXIII, Abstract #1402.2011 <strong>Kepler</strong> Science Conference - <strong>NASA</strong> Ames Research Center 189