Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
Poster Abstracts - Kepler - NASA
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
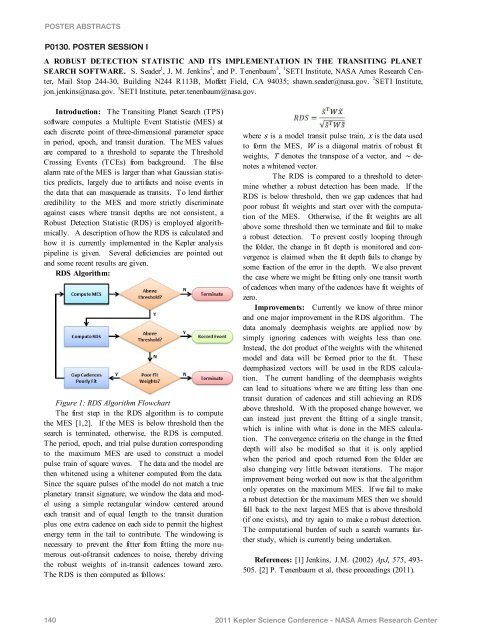
POSTER ABSTRACTSP0130. POSTER SESSION IA ROBUST DETECTION STATISTIC AND ITS IMPLEMENTATION IN THE TRANSITING PLANETSEARCH SOFTWARE. S. Seader 1 , J. M. Jenkins 2 , and P. Tenenbaum 3 , 1 SETI Institute, <strong>NASA</strong> Ames Research Center,Mail Stop 244-30, Building N244 R113B, Moffett Field, CA 94035; shawn.seader@nasa.gov. 2 SETI Institute,jon.jenkins@nasa.gov. 3 SETI Institute, peter.tenenbaum@nasa.gov.Introduction: The Transiting Planet Search (TPS)software computes a Multiple Event Statistic (MES) ateach discrete point of three-dimensional parameter spacein period, epoch, and transit duration. The MES valuesare compared to a threshold to separate the ThresholdCrossing Events (TCEs) from background. The falsealarm rate of the MES is larger than what Gaussian statisticspredicts, largely due to artifacts and noise events inthe data that can masquerade as transits. To lend furthercredibility to the MES and more strictly discriminateagainst cases where transit depths are not consistent, aRobust Detection Statistic (RDS) is employed algorithmically.A description of how the RDS is calculated andhow it is currently implemented in the <strong>Kepler</strong> analysispipeline is given. Several deficiencies are pointed outand some recent results are given.RDS Algorithm:Figure 1: RDS Algorithm FlowchartThe first step in the RDS algorithm is to computethe MES [1,2]. If the MES is below threshold then thesearch is terminated, otherwise, the RDS is computed.The period, epoch, and trial pulse duration correspondingto the maximum MES are used to construct a modelpulse train of square waves. The data and the model arethen whitened using a whitener computed from the data.Since the square pulses of the model do not match a trueplanetary transit signature, we window the data and modelusing a simple rectangular window centered aroundeach transit and of equal length to the transit durationplus one extra cadence on each side to permit the highestenergy term in the tail to contribute. The windowing isnecessary to prevent the fitter from fitting the more numerousout-of-transit cadences to noise, thereby drivingthe robust weights of in-transit cadences toward zero.The RDS is then computed as follows:where is a model transit pulse train, is the data usedto form the MES, is a diagonal matrix of robust fitweights, denotes the transpose of a vector, and denotesa whitened vector.The RDS is compared to a threshold to determinewhether a robust detection has been made. If theRDS is below threshold, then we gap cadences that hadpoor robust fit weights and start over with the computationof the MES. Otherwise, if the fit weights are allabove some threshold then we terminate and fail to makea robust detection. To prevent costly looping throughthe folder, the change in fit depth is monitored and convergenceis claimed when the fit depth fails to change bysome fraction of the error in the depth. We also preventthe case where we might be fitting only one transit worthof cadences when many of the cadences have fit weights ofzero.Improvements: Currently we know of three minorand one major improvement in the RDS algorithm. Thedata anomaly deemphasis weights are applied now bysimply ignoring cadences with weights less than one.Instead, the dot product of the weights with the whitenedmodel and data will be formed prior to the fit. Thesedeemphasized vectors will be used in the RDS calculation.The current handling of the deemphasis weightscan lead to situations where we are fitting less than onetransit duration of cadences and still achieving an RDSabove threshold. With the proposed change however, wecan instead just prevent the fitting of a single transit,which is inline with what is done in the MES calculation.The convergence criteria on the change in the fitteddepth will also be modified so that it is only appliedwhen the period and epoch returned from the folder arealso changing very little between iterations. The majorimprovement being worked out now is that the algorithmonly operates on the maximum MES. If we fail to makea robust detection for the maximum MES then we shouldfall back to the next largest MES that is above threshold(if one exists), and try again to make a robust detection.The computational burden of such a search warrants furtherstudy, which is currently being undertaken.References: [1] Jenkins, J.M. (2002) ApJ, 575, 493-505. [2] P. Tenenbaum et al, these proceedings (2011).1402011 <strong>Kepler</strong> Science Conference - <strong>NASA</strong> Ames Research Center