Understanding Map Projections
Understanding Map Projections
Understanding Map Projections
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
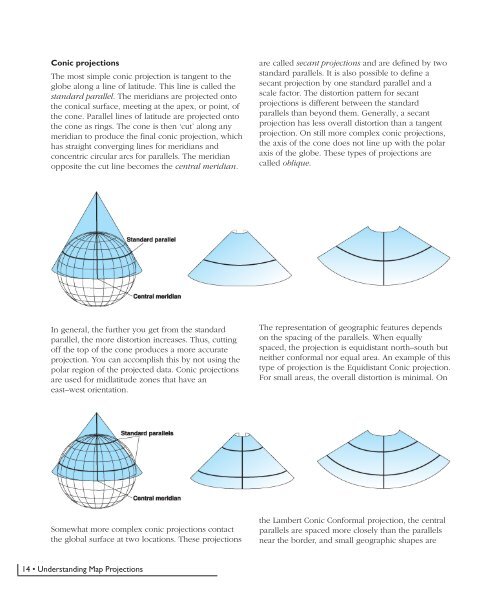
Conic projectionsThe most simple conic projection is tangent to theglobe along a line of latitude. This line is called thestandard parallel. The meridians are projected ontothe conical surface, meeting at the apex, or point, ofthe cone. Parallel lines of latitude are projected ontothe cone as rings. The cone is then ‘cut’ along anymeridian to produce the final conic projection, whichhas straight converging lines for meridians andconcentric circular arcs for parallels. The meridianopposite the cut line becomes the central meridian.are called secant projections and are defined by twostandard parallels. It is also possible to define asecant projection by one standard parallel and ascale factor. The distortion pattern for secantprojections is different between the standardparallels than beyond them. Generally, a secantprojection has less overall distortion than a tangentprojection. On still more complex conic projections,the axis of the cone does not line up with the polaraxis of the globe. These types of projections arecalled oblique.In general, the further you get from the standardparallel, the more distortion increases. Thus, cuttingoff the top of the cone produces a more accurateprojection. You can accomplish this by not using thepolar region of the projected data. Conic projectionsare used for midlatitude zones that have aneast–west orientation.The representation of geographic features dependson the spacing of the parallels. When equallyspaced, the projection is equidistant north–south butneither conformal nor equal area. An example of thistype of projection is the Equidistant Conic projection.For small areas, the overall distortion is minimal. OnSomewhat more complex conic projections contactthe global surface at two locations. These projectionsthe Lambert Conic Conformal projection, the centralparallels are spaced more closely than the parallelsnear the border, and small geographic shapes are14 • <strong>Understanding</strong> <strong>Map</strong> <strong>Projections</strong>