Understanding Map Projections
Understanding Map Projections
Understanding Map Projections
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
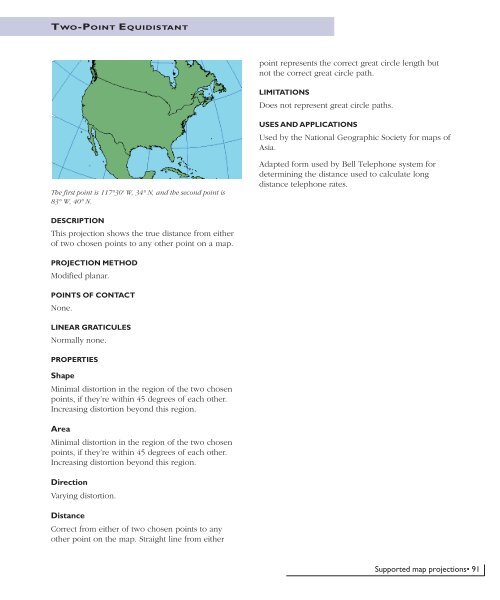
TWO-POINT EQUIDISTANTpoint represents the correct great circle length butnot the correct great circle path.LIMITATIONSDoes not represent great circle paths.USES AND APPLICATIONSUsed by the National Geographic Society for maps ofAsia.The first point is 117°30' W, 34° N, and the second point is83° W, 40° N.Adapted form used by Bell Telephone system fordetermining the distance used to calculate longdistance telephone rates.DESCRIPTIONThis projection shows the true distance from eitherof two chosen points to any other point on a map.PROJECTION METHODModified planar.POINTS OF CONTACTNone.LINEAR GRATICULESNormally none.PROPERTIESShapeMinimal distortion in the region of the two chosenpoints, if they’re within 45 degrees of each other.Increasing distortion beyond this region.AreaMinimal distortion in the region of the two chosenpoints, if they’re within 45 degrees of each other.Increasing distortion beyond this region.DirectionVarying distortion.DistanceCorrect from either of two chosen points to anyother point on the map. Straight line from eitherSupported map projections• 91