System Architecture Design
System Architecture Design
System Architecture Design
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
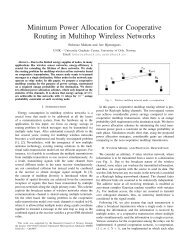
pSHIELD<strong>System</strong> <strong>Architecture</strong> <strong>Design</strong>PU2 IntroductionThe main goal of pSHIELD is to ensure that security, privacy and dependability (SPD) in the context ofintegrated and interoperating heterogeneous services, applications, systems and devices. <strong>System</strong>s andservices must be robust in the sense that an acceptable level of services is available despite theoccurrence of transient and permanent perturbations such as hardware faults, design faults, imprecisespecifications and accidental operational faults.The pSHIELD architecture composability relies on the so called SPD modules. Indeed the pSHIELDarchitecture is composed by a ‘mosaic’ of innovative SPD functionalities, each one of the consideredlayers. The pSHIELD architecture is able to derive application instantiations of the general framework,selecting statically (at design time) and dynamically (at runtime) the best SPD functionalities for achievingthe required SPD levels. In particular, referring to the abovementioned layers, the SPD modules willimplement the following functionalities:• At node layer, intelligent hardware and firmware SPD• At network layer, secure, trusted, dependable and efficient data transfer based on selfconfiguration,self-management, self-supervision and self-recovery• At middleware layer, secure and efficient resource management, inter-operation amongheterogeneous networks• At overlay layer, composabilityR&D for embedded security, intended as a system issue that must be solved at all abstraction levels(protocols, algorithms, architecture), will lead, in the framework of this task, to a coherent, composableand modular architecture for a flexible distribution of SPD information and functionalities between differentESs while supporting security and dependability characteristics.This framework in D2.3.2 aims, at the one hand, to explore the minimum set of interdependenciesbetween applications and architectures in an efficient way and to systematically classify those withrespect to SPD. On the other hand, it aims to produce a composable architecture which will include mostcritical elements, thus covering most of the SPD requirements for all the applications. This approach isexpected to produce a multi-layered architecture, where each layer consists of several hardware andsoftware SPD modules (components), since it is imperative to take into account the need for composablesecurity, privacy and dependability.The resulting architecture has to be reconfigurable, offline, meaning that mechanisms should be providedto the designer for enabling/disabling nodes in order to tailor the overall system to his needs. Furthermore,fault diagnosis and fault recovery have to be addressed both in hardware and software layers.Intra-layer and inter-layer interfaces should be defined in the system architecture to ensure the correctcommunication among the different SPD modules.PUD2.3.2Issue 5 Page 13 of 122