System Architecture Design
System Architecture Design
System Architecture Design
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
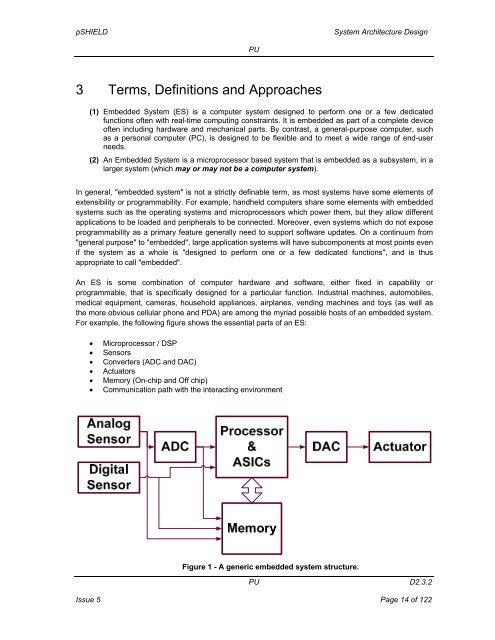
pSHIELD<strong>System</strong> <strong>Architecture</strong> <strong>Design</strong>PU3 Terms, Definitions and Approaches(1) Embedded <strong>System</strong> (ES) is a computer system designed to perform one or a few dedicatedfunctions often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete deviceoften including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, suchas a personal computer (PC), is designed to be flexible and to meet a wide range of end-userneeds.(2) An Embedded <strong>System</strong> is a microprocessor based system that is embedded as a subsystem, in alarger system (which may or may not be a computer system).In general, "embedded system" is not a strictly definable term, as most systems have some elements ofextensibility or programmability. For example, handheld computers share some elements with embeddedsystems such as the operating systems and microprocessors which power them, but they allow differentapplications to be loaded and peripherals to be connected. Moreover, even systems which do not exposeprogrammability as a primary feature generally need to support software updates. On a continuum from"general purpose" to "embedded", large application systems will have subcomponents at most points evenif the system as a whole is "designed to perform one or a few dedicated functions", and is thusappropriate to call "embedded".An ES is some combination of computer hardware and software, either fixed in capability orprogrammable, that is specifically designed for a particular function. Industrial machines, automobiles,medical equipment, cameras, household appliances, airplanes, vending machines and toys (as well asthe more obvious cellular phone and PDA) are among the myriad possible hosts of an embedded system.For example, the following figure shows the essential parts of an ES:• Microprocessor / DSP• Sensors• Converters (ADC and DAC)• Actuators• Memory (On-chip and Off chip)• Communication path with the interacting environmentFigure 1 - A generic embedded system structure.PUD2.3.2Issue 5 Page 14 of 122