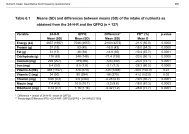
Access to substance abuse treatment in the Cape Town metropole ...
Access to substance abuse treatment in the Cape Town metropole ...
Access to substance abuse treatment in the Cape Town metropole ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
esidential areas from each of <strong>the</strong> six sub-structures of <strong>the</strong> <strong>Cape</strong> <strong>Town</strong> <strong>metropole</strong>were selected as key focus areas for sampl<strong>in</strong>g. To be selected, <strong>the</strong> area had <strong>to</strong>consistently appear <strong>in</strong> SACENDU’s list of <strong>to</strong>p ten residential areas for <strong>substance</strong>use or be identified by key <strong>in</strong>formants as an area with high levels of <strong>substance</strong>use. Selected areas also had <strong>to</strong> be classified as “Black” or “Coloured” residentialareas under <strong>the</strong> apar<strong>the</strong>id regime; have high levels of health and socialproblems; have limited <strong>in</strong>frastructure <strong>to</strong> support service delivery; and be low<strong>in</strong>comeareas.For this study, recruitment areas <strong>in</strong>cluded: Atlantis and Dunoon <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>Blaauwberg/ Nor<strong>the</strong>rn sub-structure, Delft and Khayelitsha <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Tygerberg substructure,Eersterivier and Wallacedene <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Oostenberg/Eastern sub-structure,Macassar and Lowandle <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Helderberg sub-structure, Langa and Retreat <strong>in</strong><strong>the</strong> Sou<strong>the</strong>rn Pen<strong>in</strong>sula sub-structure, and Mitchell’s Pla<strong>in</strong> and Gugulethu <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>Central sub-structure of <strong>the</strong> <strong>Cape</strong> <strong>Town</strong> <strong>metropole</strong>.3.3.1.4. Characteristics of <strong>the</strong> f<strong>in</strong>al sampleA non-random, snowball sample of 989 participants was drawn from <strong>the</strong> selectedrecruitment areas. The f<strong>in</strong>al sample consisted of 434 cases and 555 controls. Of<strong>the</strong>se controls, approximately 46 were selected from each recruitment area. Chisquaretests of association reveal that cases and controls did not differ bygender, or race. Demographic data for this study are shown <strong>in</strong> Table 2.3.3.2. Procedures3.3.2.1. Pilot test<strong>in</strong>gPrior <strong>to</strong> <strong>in</strong>itiat<strong>in</strong>g phase 1, <strong>the</strong> <strong>Access</strong> <strong>to</strong> Treatment Survey Questionnaire (ATQ)was pilot-tested among 40 <strong>substance</strong> users from two his<strong>to</strong>rically disadvantagedcommunities <strong>in</strong> <strong>Cape</strong> <strong>Town</strong>. Feedback from <strong>the</strong> pilot-test<strong>in</strong>g allowed researchers<strong>to</strong> ref<strong>in</strong>e <strong>the</strong> ATQ and change problematically worded items prior <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> ma<strong>in</strong>study. Pilot-test<strong>in</strong>g also allowed <strong>the</strong> reliability of <strong>the</strong> scales that comprise <strong>the</strong> ATQ<strong>to</strong> be established for a South African <strong>substance</strong>-us<strong>in</strong>g population. As feedbackfrom fieldworkers, key <strong>in</strong>formants and participants revealed that most <strong>in</strong>dividuals26