5 The role of quorum-sensing in the virulence of Pseudomonas ...
5 The role of quorum-sensing in the virulence of Pseudomonas ...
5 The role of quorum-sensing in the virulence of Pseudomonas ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
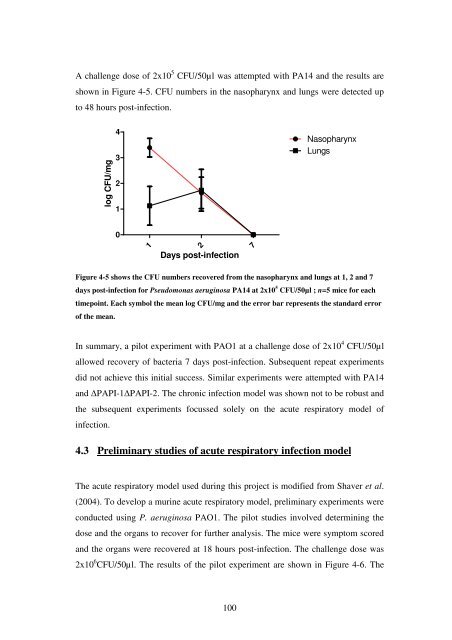
A challenge dose <strong>of</strong> 2x10 5 CFU/50µl was attempted with PA14 and <strong>the</strong> results are<br />
shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 4-5. CFU numbers <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> nasopharynx and lungs were detected up<br />
to 48 hours post-<strong>in</strong>fection.<br />
log CFU/mg<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
1<br />
2<br />
Days post-<strong>in</strong>fection<br />
100<br />
7<br />
Nasopharynx<br />
Lungs<br />
Figure 4-5 shows <strong>the</strong> CFU numbers recovered from <strong>the</strong> nasopharynx and lungs at 1, 2 and 7<br />
days post-<strong>in</strong>fection for <strong>Pseudomonas</strong> aerug<strong>in</strong>osa PA14 at 2x10 5 CFU/50µl ; n=5 mice for each<br />
timepo<strong>in</strong>t. Each symbol <strong>the</strong> mean log CFU/mg and <strong>the</strong> error bar represents <strong>the</strong> standard error<br />
<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> mean.<br />
In summary, a pilot experiment with PAO1 at a challenge dose <strong>of</strong> 2x10 4 CFU/50µl<br />
allowed recovery <strong>of</strong> bacteria 7 days post-<strong>in</strong>fection. Subsequent repeat experiments<br />
did not achieve this <strong>in</strong>itial success. Similar experiments were attempted with PA14<br />
and ∆PAPI-1∆PAPI-2. <strong>The</strong> chronic <strong>in</strong>fection model was shown not to be robust and<br />
<strong>the</strong> subsequent experiments focussed solely on <strong>the</strong> acute respiratory model <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>fection.<br />
4.3 Prelim<strong>in</strong>ary studies <strong>of</strong> acute respiratory <strong>in</strong>fection model<br />
<strong>The</strong> acute respiratory model used dur<strong>in</strong>g this project is modified from Shaver et al.<br />
(2004). To develop a mur<strong>in</strong>e acute respiratory model, prelim<strong>in</strong>ary experiments were<br />
conducted us<strong>in</strong>g P. aerug<strong>in</strong>osa PAO1. <strong>The</strong> pilot studies <strong>in</strong>volved determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong><br />
dose and <strong>the</strong> organs to recover for fur<strong>the</strong>r analysis. <strong>The</strong> mice were symptom scored<br />
and <strong>the</strong> organs were recovered at 18 hours post-<strong>in</strong>fection. <strong>The</strong> challenge dose was<br />
2x10 6 CFU/50µl. <strong>The</strong> results <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> pilot experiment are shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 4-6. <strong>The</strong>