PHYSICS
n - susliks.lv
n - susliks.lv
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.3.4. The Lever<br />
A lever is the simplest mechanism by which it is possible to<br />
balance a larger force by a lesser one. A lever consists of a plank<br />
which pivots at a point called the fulcrum. There are three forces<br />
acting on the plank: the downward force (F) used to try to lift<br />
the heavy mass (M), the reaction force (R) at the fulcrum, and<br />
the force (P) arising from the gravitational pull on the body<br />
(fig. 3.3).<br />
R<br />
M<br />
Muscle<br />
(J<br />
Humeral<br />
bone<br />
p<br />
5x<br />
F<br />
'------<br />
/]<br />
Fig. 3.3. A lever which consists of a plank of mass M pivoted<br />
near its end can be used to mechanical advantage; /] and /] are the<br />
lever arms; R is the reaction force at the fulcrum<br />
Two of these forces, F and P, tend to rotate the plank about<br />
the fulcrum, the extent of which depends on the product of the<br />
force and its perpendicular distance from the fulcrum. The<br />
product is called the moment of the force and the plank will be in<br />
equilibrium when the clockwise and counterclockwise moments<br />
are equal:<br />
Fl, = PI]<br />
P<br />
(3.31)<br />
Hence, F will be small if I] is small, in which case the point<br />
of pivot should be as near the body as possible. The ratio PI/F is<br />
known as the mechanical advantage of the lever.<br />
The biceps muscles and the jaws are examples of a lever mechanism<br />
in a living organism.<br />
28<br />
a<br />
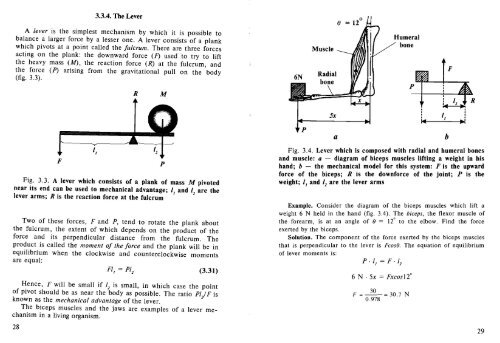
Fig. 3.4. Lever which is composed with radial and humeral bones<br />
and muscle: a - diagram of biceps muscles lifting a weight in his<br />
hand; b - the mechanical model for this system: F is the upward<br />
force of the biceps; R is the downforce of the joint; P is the<br />
weight; I] and /] are the lever arms<br />
Example. Consider the diagram of the biceps muscles which lift a<br />
weight 6 N held in the hand (fig. 3.4). The biceps, the flexor muscle of<br />
the forearm, is at an angle of (J = 12° to the elbow. Find the force<br />
exerted by the biceps.<br />
Solution. The component of the force exerted by the biceps muscles<br />
that is perpendicular to the lever is Feese. The equation of equilibrium<br />
of lever moments is:<br />
p. II = F· I]<br />
6 N . 5x = Fxcosl2°<br />
F = 30<br />
0.978 = 30.7 N<br />
b<br />
29