PHYSICS
n - susliks.lv
n - susliks.lv
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
t1 cp = -f B Eds = - Ed (15.9)<br />
A<br />
or<br />
E = _ t1cp<br />
d<br />
(15.10)<br />
where the minus sign results from the fact that point B is at a<br />
lower potential than point A.<br />
With a non-uniform electric field, from the Equation (15.7)<br />
we can express the potential difference (dcp) between two points a<br />
distance (ds) apart as:<br />
dcp = -E· ds (15.11)<br />
If the electric field has only one component (E), then E-ds =<br />
= Exdx. Therefore, Equation (15.7) becomes dip = - Exdx or:<br />
dcp<br />
Ex = - dx (15.12)<br />
Therefore, the electric field is equal to the negative of the derivative<br />
of the potential with respect to some coordinate.<br />
In general, the electric potential is a function of all three spatial<br />
coordinates. If cp (r) = cp (x,y,z) is given in the rectangular<br />
coordinates, the electric field components are given by:<br />
E = - dcp E = _ dcp E = _ dcp<br />
x dX' Y dy' Z dZ (15.13)<br />
F = qE = mii (15.14)<br />
where m is the mass of the particle. The acceleration of the<br />
particle is therefore given by:<br />
a = qE (15.15)<br />
m<br />
15.2.7. Oscillograph<br />
The oscillograph is an electronic instrument widely used in<br />
making electrical measurements when rapidly changing electrical<br />
signals are studied, e.g. nerve action potentials or electrical<br />
signals in plants. The main component of the oscillograph is the<br />
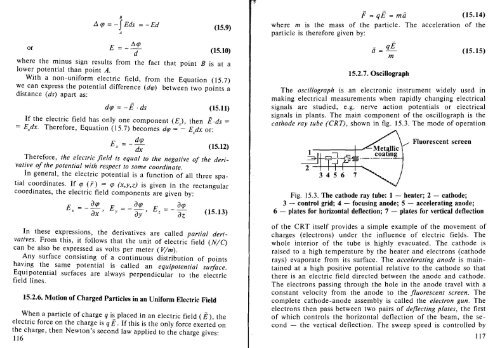
cathode ray tube (CRT), shown in fig. 15.3. The mode of operation<br />
Fluorescent screen<br />
Fig. 15.3. The cathode ray tube: 1 - heater; 2 - cathode;<br />
3 - control grid; 4 - focusing anode; 5 - accelerating anode;<br />
6 - plates for horizontal deflection; 7 - plates for vertical deflection<br />
In these expressions, the derivatives are called partial derivatives.<br />
From this, it follows that the unit of electric field (Nlc)<br />
can be also be expressed as volts per meter (Vim).<br />
Any surface consisting of a continuous distribution of points<br />
having the same potential is called an equipotential surface.<br />
Equipotential surfaces are always perpendicular to the electric<br />
field lines.<br />
15.2.6. Motion of Charged Particles in an Uniform Electric Field<br />
When a particle of charge q is placed in an electric field (E), the<br />
electric force on the charge is q E. If this is the only force exerted on<br />
the charge, then Newton's second law applied to the charge gives:<br />
of the CRT itself provides a simple example of the movement of<br />
charges (electrons) under the influence of electric fields. The<br />
whole interior of the tube is highly evacuated. The cathode is<br />
raised to a high temperature by the heater and electrons (cathode<br />
rays) evaporate from its surface. The accelerating anode is maintained<br />
at a high positive potential relative to the cathode so that<br />
there is an electric field directed between the anode and cathode.<br />
The electrons passing through the hole in the anode travel with a<br />
constant velocity from the anode to the fluorescent screen. The<br />
complete cathode-anode assembly is called the electron gun. The<br />
electrons then pass between two pairs of deflecting plates, the first<br />
of which controls the horizontal deflection of the beam, the second<br />
- the vertical deflection. The sweep speed is controlled by<br />
116 117