Banking for 7 billion and 7 million
New challenges and opportunities of globalization Global Investor, 03/2006 Credit Suisse
New challenges and opportunities of globalization
Global Investor, 03/2006
Credit Suisse
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
GLOBAL INVESTOR 3.06 Basics — 28<br />
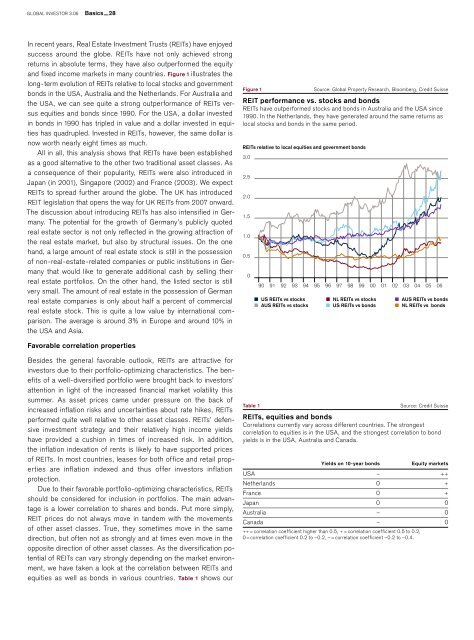
In recent years, Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) have enjoyed<br />
success around the globe. REITs have not only achieved strong<br />
returns in absolute terms, they have also outper<strong>for</strong>med the equity<br />
<strong>and</strong> fixed income markets in many countries. Figure 1 illustrates the<br />
long-term evolution of REITs relative to local stocks <strong>and</strong> government<br />
bonds in the USA, Australia <strong>and</strong> the Netherl<strong>and</strong>s. For Australia <strong>and</strong><br />
the USA, we can see quite a strong outper<strong>for</strong>mance of REITs versus<br />
equities <strong>and</strong> bonds since 1990. For the USA, a dollar invested<br />
in bonds in 1990 has tripled in value <strong>and</strong> a dollar invested in equities<br />
has quadrupled. Invested in REITs, however, the same dollar is<br />
now worth nearly eight times as much.<br />
All in all, this analysis shows that REITs have been established<br />
as a good alternative to the other two traditional asset classes. As<br />
a consequence of their popularity, REITs were also introduced in<br />
Japan (in 2001), Singapore (2002) <strong>and</strong> France (2003). We expect<br />
REITs to spread further around the globe. The UK has introduced<br />
REIT legislation that opens the way <strong>for</strong> UK REITs from 2007 onward.<br />
The discussion about introducing REITs has also intensified in Germany.<br />
The potential <strong>for</strong> the growth of Germany’s publicly quoted<br />
real estate sector is not only reflected in the growing attraction of<br />
the real estate market, but also by structural issues. On the one<br />
h<strong>and</strong>, a large amount of real estate stock is still in the possession<br />
of non-real-estate-related companies or public institutions in Germany<br />
that would like to generate additional cash by selling their<br />
real estate portfolios. On the other h<strong>and</strong>, the listed sector is still<br />
very small. The amount of real estate in the possession of German<br />
real estate companies is only about half a percent of commercial<br />
real estate stock. This is quite a low value by international comparison.<br />
The average is around 3% in Europe <strong>and</strong> around 10% in<br />
the USA <strong>and</strong> Asia.<br />
Figure 1<br />
REITs relative to local equities <strong>and</strong> government bonds<br />
3.0<br />
2.5<br />
2.0<br />
1.5<br />
1.0<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06<br />
US REITs vs stocks<br />
AUS REITs vs stocks<br />
Source: Global Property Research, Bloomberg, Credit Suisse<br />
REIT per<strong>for</strong>mance vs. stocks <strong>and</strong> bonds<br />
REITs have outper<strong>for</strong>med stocks <strong>and</strong> bonds in Australia <strong>and</strong> the USA since<br />
1990. In the Netherl<strong>and</strong>s, they have generated around the same returns as<br />
local stocks <strong>and</strong> bonds in the same period.<br />
NL REITs vs stocks<br />
US REITs vs bonds<br />
AUS REITs vs bonds<br />
NL REITs vs bonds<br />
Favorable correlation properties<br />
Besides the general favorable outlook, REITs are attractive <strong>for</strong><br />
investors due to their portfolio-optimizing characteristics. The benefits<br />
of a well-diversified portfolio were brought back to investors’<br />
attention in light of the increased financial market volatility this<br />
summer. As asset prices came under pressure on the back of<br />
increased inflation risks <strong>and</strong> uncertainties about rate hikes, REITs<br />
per<strong>for</strong>med quite well relative to other asset classes. REITs’ defensive<br />
investment strategy <strong>and</strong> their relatively high income yields<br />
have provided a cushion in times of increased risk. In addition,<br />
the inflation indexation of rents is likely to have supported prices<br />
of REITs. In most countries, leases <strong>for</strong> both office <strong>and</strong> retail properties<br />
are inflation indexed <strong>and</strong> thus offer investors inflation<br />
protection.<br />
Due to their favorable portfolio-optimizing characteristics, REITs<br />
should be considered <strong>for</strong> inclusion in portfolios. The main advantage<br />
is a lower correlation to shares <strong>and</strong> bonds. Put more simply,<br />
REIT prices do not always move in t<strong>and</strong>em with the movements<br />
of other asset classes. True, they sometimes move in the same<br />
direction, but often not as strongly <strong>and</strong> at times even move in the<br />
opposite direction of other asset classes. As the diversification potential<br />
of REITs can vary strongly depending on the market environment,<br />
we have taken a look at the correlation between REITs <strong>and</strong><br />
equities as well as bonds in various countries. Table 1 shows our<br />
Table 1<br />
Source: Credit Suisse<br />
REITs, equities <strong>and</strong> bonds<br />
Correlations currently vary across different countries. The strongest<br />
correlation to equities is in the USA, <strong>and</strong> the strongest correlation to bond<br />
yields is in the USA, Australia <strong>and</strong> Canada.<br />
Yields on 10-year bonds<br />
Equity markets<br />
USA – ++<br />
Netherl<strong>and</strong>s 0 +<br />
France 0 +<br />
Japan 0 0<br />
Australia – 0<br />
Canada – 0<br />
++ = correlation coefficient higher than 0.5, + = correlation coefficient 0.5 to 0.2,<br />
0 = correlation coefficient 0.2 to –0.2, – = correlation coefficient –0.2 to –0.4.