Bayesian Programming and Learning for Multi-Player Video Games ...
Bayesian Programming and Learning for Multi-Player Video Games ...
Bayesian Programming and Learning for Multi-Player Video Games ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
M<br />
Op t-1<br />
M<br />
Op t<br />
V<br />
T<br />
0,1<br />
BT O N<br />
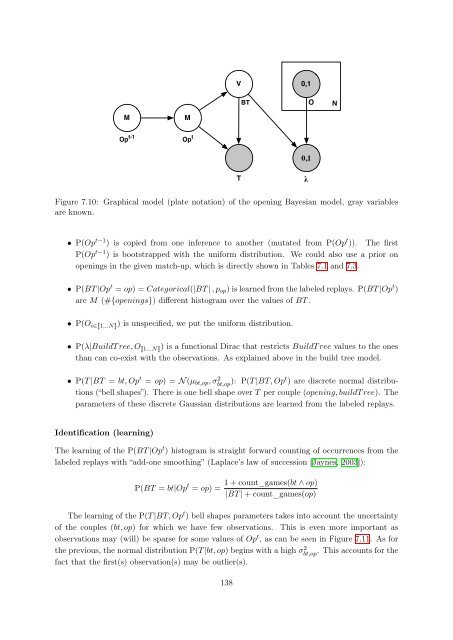
Figure 7.10: Graphical model (plate notation) of the opening <strong>Bayesian</strong> model, gray variables<br />
are known.<br />
• P(Op t−1 ) is copied from one inference to another (mutated from P(Op t )). The first<br />
P(Op t−1 ) is bootstrapped with the uni<strong>for</strong>m distribution. We could also use a prior on<br />
openings in the given match-up, which is directly shown in Tables 7.1 <strong>and</strong> 7.3.<br />
• P(BT |Op t = op) = Categorical(|BT | , pop) is learned from the labeled replays. P(BT |Op t )<br />
are M (#{openings}) different histogram over the values of BT .<br />
• P(O i∈�1...N�) is unspecified, we put the uni<strong>for</strong>m distribution.<br />
• P(λ|BuildT ree, O �1...N�) is a functional Dirac that restricts BuildT ree values to the ones<br />
than can co-exist with the observations. As explained above in the build tree model.<br />
• P(T |BT = bt, Op t = op) = N (µbt,op, σ 2 bt,op ): P(T |BT, Opt ) are discrete normal distributions<br />
(“bell shapes”). There is one bell shape over T per couple (opening, buildT ree). The<br />
parameters of these discrete Gaussian distributions are learned from the labeled replays.<br />
Identification (learning)<br />
The learning of the P(BT |Op t ) histogram is straight <strong>for</strong>ward counting of occurrences from the<br />
labeled replays with “add-one smoothing” (Laplace’s law of succession [Jaynes, 2003]):<br />
P(BT = bt|Op t = op) =<br />
0,1<br />
1 + count_games(bt ∧ op)<br />
|BT | + count_games(op)<br />
The learning of the P(T |BT, Opt ) bell shapes parameters takes into account the uncertainty<br />
of the couples (bt, op) <strong>for</strong> which we have few observations. This is even more important as<br />
observations may (will) be sparse <strong>for</strong> some values of Opt , as can be seen in Figure 7.11. As <strong>for</strong><br />
the previous, the normal distribution P(T |bt, op) begins with a high σ2 bt,op . This accounts <strong>for</strong> the<br />
fact that the first(s) observation(s) may be outlier(s).<br />
138<br />
λ