Nadir Arada - (Cálculo Numérico) - Portal de docentes FCT/UNL
Nadir Arada - (Cálculo Numérico) - Portal de docentes FCT/UNL
Nadir Arada - (Cálculo Numérico) - Portal de docentes FCT/UNL
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Problema <strong>de</strong> Cauchy Derivada numérica Aproximação Euler Estabilda<strong>de</strong> Runge-Kutta 2 Runge-Kutta 4<br />
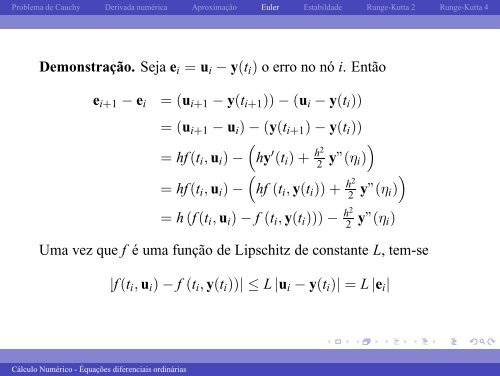
Demonstração. Seja ei = ui − y(ti) o erro no nó i. Então<br />
ei+1 − ei = (ui+1 − y(ti+1)) − (ui − y(ti))<br />
= (ui+1 − ui) − (y(ti+1) − y(ti))<br />
<br />
= hf(ti, ui) − hy ′ (ti) + h2<br />
2 y”(ηi)<br />
<br />
<br />
= hf(ti, ui) − hf (ti, y(ti)) + h2<br />
2 y”(ηi)<br />
<br />
= h(f(ti, ui) − f (ti, y(ti))) − h2<br />
2 y”(ηi)<br />
Uma vez que f é uma função <strong>de</strong> Lipschitz <strong>de</strong> constante L, tem-se<br />
<strong>Cálculo</strong> <strong>Numérico</strong> - Équações diferenciais ordinárias<br />
|f(ti, ui) − f (ti, y(ti))| ≤ L |ui − y(ti)| = L |ei|