- Page 1 and 2: Raport de cercetare - lucrare în e
- Page 3 and 4: 2. Scop şi obiective Scopul proiec
- Page 5 and 6: abordare integrată în căutarea r
- Page 7 and 8: • cu acces parţial restricţiona
- Page 9 and 10: 2007A1. Planificarea activităţilo
- Page 11 and 12: 2 Y = 0.852 -1 =a+bX -1 (Y -1 -a-bX
- Page 13 and 14: PCB128 136.38 -3.4116 0.7761 PCB129
- Page 15 and 16: ISDmsHt lADrtHg Y Equation Residue
- Page 17 and 18: ISDmsHt lADrtHg Y Equation Residue
- Page 19 and 20: ISDmsHt lADrtHg Y Equation Residue
- Page 21 and 22: Tabelul următor prezintă sintetic
- Page 23 and 24: d_RSD INF 2.6057 d_Volum Matricea p
- Page 25 and 26: 30 1.02 0.63 1.75 2.67 160 31 1.14
- Page 27 and 28: Matricea valorilor coeficientului d
- Page 29 and 30: evaluare sistematică pentru identi
- Page 31 and 32: introductivă în subiectul prezent
- Page 33 and 34: Studio (al companiei Accelrys) a pe
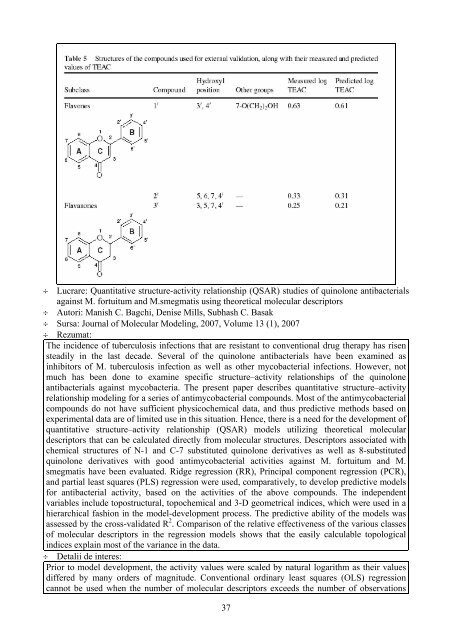
- Page 35: Setting the weights equal to 1 give
- Page 39 and 40: compound ranking in the database. A
- Page 41 and 42: vectors based on the cloning strate
- Page 43 and 44: "Recent Advances in Synthesis and C
- Page 45 and 46: will be highly inactive, moderately
- Page 47 and 48: Publication Frequency: 8 issues per
- Page 49 and 50: of strand breaks and when they do o
- Page 51 and 52: ibonucleotide reductase Journal of
- Page 53 and 54: scenarios are to be compared, e.g.
- Page 55 and 56: hydrazones • ligand-based drug de
- Page 57 and 58: modalitatea de culegere, colectare
- Page 59 and 60: ÷ Transversală: studierea unui e
- Page 61 and 62: 9 10 12 8 1 4 3 2 2 15 8 5 4 3 4 8
- Page 63 and 64: 2 1 1 2 3 2 0 1 4 3 2 2 5 4 2 0 6 5
- Page 65 and 66: 10 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 11 0 0 0 1
- Page 67 and 68: 12 0 0 0 1 0 0 L12 Factori (nivele)
- Page 69 and 70: 3 1 ×2 4 A(3) B(2) C(2) D(2) E(2)
- Page 71 and 72: 9 8 0 2 2 2 1 1 10 9 1 2 1 1 0 0 11
- Page 73 and 74: 7 1 4 1 1 2 4 8 2 2 3 4 1 1 9 3 2 1
- Page 75 and 76: 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0
- Page 77 and 78: 11 10 9 9 4 11 12 11 8 10 3 13 13 1
- Page 79 and 80: ÷ Endorelaţie binară (`2-e-r`):
- Page 81 and 82: muchiei e); ponderile pentru vârfu
- Page 83 and 84: ale grafului; între numărul de fe
- Page 85 and 86: Detur d5,1=3; d5,2=3; d5,3=2; d5,4=
- Page 87 and 88:
3 1 024220000 1145 4 0 022100222 11
- Page 89 and 90:
o ΣA(·) 2 : 231; o Matricea: De 1
- Page 91 and 92:
(10, 3) [10, 6, 3] {7, 10, 11} (3,
- Page 93 and 94:
11 0.250 0.333 0.333 0.333 0.250 0.
- Page 95 and 96:
(5, 11) [5, 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 11
- Page 97 and 98:
(1, 11) [1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11] {1, 4,
- Page 99 and 100:
(9, 11) [9, 8, 7, 11] {1, 2, 3, 4,
- Page 101 and 102:
(3, 8) [3, 6, 10, 11, 7, 8] {1, 2,
- Page 103 and 104:
6 0.167 0.167 0.167 0.167 0.167 0.0
- Page 105 and 106:
5 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.500 0.000 0.3
- Page 107 and 108:
Tabelul 10. Matricea caracteristic
- Page 109 and 110:
10 6 7 8 9 10 11 11 6 7 8 9 10 11 6
- Page 111 and 112:
Astfel, adaptând principiul I al t
- Page 113 and 114:
Din formula sa de definiţie dS = d
- Page 115 and 116:
produsul final al întregului lanţ
- Page 117 and 118:
Tabelul 16. Cât de dulci sunt zaha
- Page 119 and 120:
÷ CSLS; ÷ Cyberlipid Center; ÷ D
- Page 121 and 122:
÷ STING Millenium Suite; ÷ wwPDB;
- Page 123 and 124:
pentru care algoritmul performează
- Page 125 and 126:
scopul maximizării randamentului d
- Page 127 and 128:
solului, calitatea vremii, manageme
- Page 129 and 130:
Fragmentation criteria Fragment of
- Page 131 and 132:
o Se încrucişează Genotip1 cu Ge
- Page 133 and 134:
Measures of Disease in Health Resea
- Page 135 and 136:
Generarea întâmplătoare stratifi
- Page 137 and 138:
Functional Networks Noelia Sánchez
- Page 139 and 140:
o SVMs application to protein secon
- Page 141 and 142:
Meta-learning for Algorithm Recomme
- Page 143 and 144:
Similarity Assessment with PDR-FP
- Page 145 and 146:
• Representations of a molecular
- Page 147 and 148:
Introduction - Non HTS Hit Recognit
- Page 149 and 150:
Post-processing: Visual Inspection
- Page 151 and 152:
PCB013 146.55 -2.7348 0.3315 0.3241
- Page 153 and 154:
PCB113 136.08 -3.2367 0.5862 0.5861
- Page 155 and 156:
Regression 1 6.730776811 6.730777 7
- Page 157 and 158:
Metoda Formula intervalului de înc
- Page 159 and 160:
1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 Metoda ArcS 0
- Page 161 and 162:
Metoda AvADA(0) AvADA(1) AvADS(0) A
- Page 163 and 164:
12 11.01 9.99 10 8 6 4 2 0 6 5 4 3
- Page 165 and 166:
Planificarea activităţilor experi
- Page 167 and 168:
o Generalized functions; o Operator
- Page 169 and 170:
approaches of QSAR modeling o Sessi
- Page 171 and 172:
Bookhaven pe care o transferă prog
- Page 173 and 174:
1.21739507388622E+000 y= 7.38149868
- Page 175 and 176:
20 020_3613389 7.783 -1.627 5.661 0
- Page 177 and 178:
} function atom_info($atom,&$cnv_to
- Page 179 and 180:
}else{ } } $this->tmp_dist=array();
- Page 181 and 182:
} } return "({".implode(",",$this->
- Page 183 and 184:
if($this->p12_2) $this->f[57] =$thi
- Page 185 and 186:
$fr_f_t=pow(pow($fr_f_x,2)+pow($fr_
- Page 187 and 188:
} } $this->f[$a]=$ret; } Interacţi
- Page 189 and 190:
÷ 2 tipuri de selecţii ale valori
- Page 191 and 192:
} $ret[$j][$k]=array(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.
- Page 193 and 194:
if(!$q){ } echo($query." :ERROR!\r\
- Page 195 and 196:
} unset($a); $query="INSERT INTO `"
- Page 197 and 198:
$ok=$this->check_finite();if(!$ok)r
- Page 199 and 200:
$q=mysql_query($query_prop."'".$mdf
- Page 201 and 202:
2005-RIMC; Jäntschi & Bolboacă, 2
- Page 203 and 204:
0.918 0.9 5 14 23110_ 69 332064 837
- Page 205 and 206:
0.9665 0.9525 4 30 33504 73 r = 0.9
- Page 207 and 208:
20 41521_ lNMrEQg*0.336843860556055
- Page 209 and 210:
54 DevMTOp25_ y=1.893045064859439+
- Page 211 and 212:
82 19654_ lIDRFMg*-1.31755354516111
- Page 213 and 214:
y=3.463929176330566+ ABDmtQg*-13.01
- Page 215 and 216:
iBMmwHg*1195.781250000000000+ iFPME
- Page 217 and 218:
161 15aacidsHyd_ lSDmwMt*6.37250438
- Page 219 and 220:
Relaţii semicantitative structură
- Page 221 and 222:
MDFV (Jäntschi şi Bolboacă, 2008
- Page 223 and 224:
SAPF (©2009) CF:3 DO:2 AP:5 DP:6 P
- Page 225 and 226:
N0) fenotipurilor între generaţii
- Page 227 and 228:
adevăr (T/F) pentru fiecare operat
- Page 229 and 230:
S5 String[255] Şir de maxim 255 ca
- Page 231 and 232:
end; with(MDF)do repeat CF_Rs;SA_Fr
- Page 233 and 234:
sfs_FITNESS_strategy= proportional/
- Page 235 and 236:
parametrul statistic descriptiv mx
- Page 237 and 238:
d_n:S9; Variabilă folosită la pen
- Page 239 and 240:
(s:S9):B0T; configurare a execuţie
- Page 241 and 242:
; ÷ mută părinţi cu probabilita
- Page 243 and 244:
procedure SL_QSr (i,j:I0T); procedu
- Page 245 and 246:
XX_min = XX_max = XX_avg = XX (XX =
- Page 247 and 248:
$p_max[$i]=1.0*$m-1.0*$m*$tdist->_g
- Page 249 and 250:
$d[$i][$k++]=$c[$i][$j]; for($i=0;$
- Page 251 and 252:
for($i=0;$i
- Page 253 and 254:
mat_means($n,$m,$y,$x,$ma,$mb); red
- Page 255 and 256:
} if(strlen($s)>0) $t[]=$s; return
- Page 257 and 258:
este necesar ca să se asume ipotez
- Page 259 and 260:
6(( b − a + 1) Asimetria; excesul
- Page 261 and 262:
Minim; Maxim 0; ∞ Funcţia de pro
- Page 263 and 264:
Varianţa Var γ1 (nX-1)σ 2 /nX 2
- Page 265 and 266:
Σ1≤i≤m(Ŷi-Yi) 2 → min. (3)
- Page 267 and 268:
Tabelul 24. Valorile optimizate ale
- Page 269 and 270:
eroare m(n-1) 2 m ⎛ n ⎛ n ⎞
- Page 271 and 272:
http://l.academicdirect.ro/Chemistr
- Page 273 and 274:
http://l.academicdirect.ro/Chemistr
- Page 275 and 276:
http://l.academicdirect.ro/Chemistr
- Page 277 and 278:
73 la convergenţă folosind un alg
- Page 279 and 280:
Cl(n) Cl (n) PCBs: Seria bifenililo
- Page 281 and 282:
PCB027 Cl Cl Cl 5.447 PCB028 Cl Cl
- Page 283 and 284:
PCB071 Cl Cl Cl Cl 5.987 PCB072 Cl
- Page 285 and 286:
PCB110 Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl 6.532 PCB111
- Page 287 and 288:
PCB151 Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl 6.647 PCB1
- Page 289 and 290:
PCB191 Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl 7.557 P
- Page 291 and 292:
O altă remarcă se poate face cu p
- Page 293 and 294:
al eşantionului pe care o induc me
- Page 295 and 296:
PmkEt 1 26 26 sDDJEg 1 26 26 MDDKHt
- Page 297 and 298:
86 Abateri semnificative statistic
- Page 299 and 300:
Generaţii ce produc evoluţii (num
- Page 301 and 302:
Rar (D, P) (D, T) Figura 2. Cât de
- Page 303 and 304:
2010A5. Construirea bazei de date c
- Page 305 and 306:
Portalul "MDF" Portalul "Statistics
- Page 307 and 308:
(Bolboacă & Jäntschi, 2007-AAHS):
- Page 309 and 310:
Environment, Applied Medical Inform
- Page 311 and 312:
AcademicDirect, ISSN 1583-1078, www
- Page 313 and 314:
Observable: Maximum Likelihood Esti
- Page 315 and 316:
and Veterinary Medicine Cluj-Napoca
- Page 317 and 318:
Relative Response Factor using Mole