22. Workshop für experimentelle und klinische Lebertransplantation ...
22. Workshop für experimentelle und klinische Lebertransplantation ...
22. Workshop für experimentelle und klinische Lebertransplantation ...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
Transplantationsmedizin<br />
Supplement I – 2011, S. 33<br />
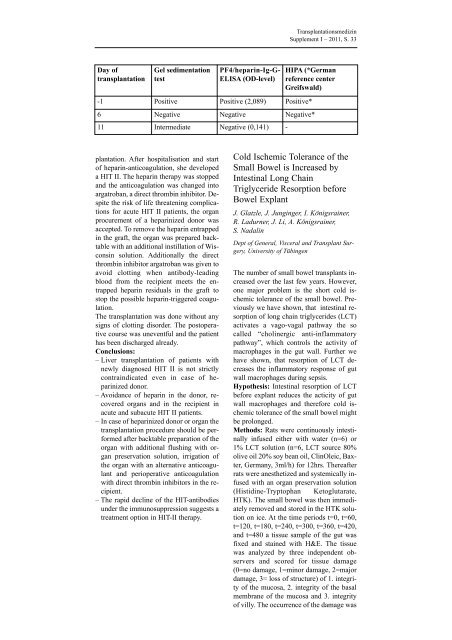
Day of<br />
transplantation<br />
Gel sedimentation<br />
test<br />
PF4/heparin-Ig-G-<br />
ELISA (OD-level)<br />
HIPA (*German<br />
reference center<br />
Greifswald)<br />
-1 Positive Positive (2,089) Positive*<br />
6 Negative Negative Negative*<br />
11 Intermediate Negative (0,141) -<br />
plantation. After hospitalisation and start<br />
of heparin-anticoagulation, she developed<br />
a HIT II. The heparin therapy was stopped<br />
and the anticoagulation was changed into<br />
argatroban, a direct thrombin inhibitor. Despite<br />
the risk of life threatening complications<br />
for acute HIT II patients, the organ<br />
procurement of a heparinized donor was<br />
accepted. To remove the heparin entrapped<br />
in the graft, the organ was prepared backtable<br />
with an additional instillation of Wisconsin<br />
solution. Additionally the direct<br />
thrombin inhibitor argatroban was given to<br />
avoid clotting when antibody-leading<br />
blood from the recipient meets the entrapped<br />
heparin residuals in the graft to<br />
stop the possible heparin-triggered coagulation.<br />
The transplantation was done without any<br />
signs of clotting disorder. The postoperative<br />
course was uneventful and the patient<br />
has been discharged already.<br />
Conclusions:<br />
– Liver transplantation of patients with<br />
newly diagnosed HIT II is not strictly<br />
contraindicated even in case of heparinized<br />
donor.<br />
– Avoidance of heparin in the donor, recovered<br />
organs and in the recipient in<br />
acute and subacute HIT II patients.<br />
– In case of heparinized donor or organ the<br />
transplantation procedure should be performed<br />
after backtable preparation of the<br />
organ with additional flushing with organ<br />
preservation solution, irrigation of<br />
the organ with an alternative anticoagulant<br />
and perioperative anticoagulation<br />
with direct thrombin inhibitors in the recipient.<br />
– The rapid decline of the HIT-antibodies<br />
<strong>und</strong>er the immunosuppression suggests a<br />
treatment option in HIT-II therapy.<br />
Cold Ischemic Tolerance of the<br />
Small Bowel is Increased by<br />
Intestinal Long Chain<br />
Triglyceride Resorption before<br />
Bowel Explant<br />
J. Glatzle, J. Junginger, I. Königsrainer,<br />
R. Ladurner, J. Li, A. Königsrainer,<br />
S. Nadalin<br />
Dept of General, Visceral and Transplant Surgery,<br />
University of Tübingen<br />
The number of small bowel transplants increased<br />
over the last few years. However,<br />
one major problem is the short cold ischemic<br />
tolerance of the small bowel. Previously<br />
we have shown, that intestinal resorption<br />
of long chain triglycerides (LCT)<br />
activates a vago-vagal pathway the so<br />
called “cholinergic anti-inflammatory<br />
pathway”, which controls the activity of<br />
macrophages in the gut wall. Further we<br />
have shown, that resorption of LCT decreases<br />
the inflammatory response of gut<br />
wall macrophages during sepsis.<br />
Hypothesis: Intestinal resorption of LCT<br />
before explant reduces the acticity of gut<br />
wall macrophages and therefore cold ischemic<br />
tolerance of the small bowel might<br />
be prolonged.<br />
Methods: Rats were continuously intestinally<br />
infused either with water (n=6) or<br />
1% LCT solution (n=6, LCT source 80%<br />
olive oil 20% soy bean oil, ClinOleic, Baxter,<br />
Germany, 3ml/h) for 12hrs. Thereafter<br />
rats were anesthetized and systemically infused<br />
with an organ preservation solution<br />
(Histidine-Tryptophan Ketoglutarate,<br />
HTK). The small bowel was then immediately<br />
removed and stored in the HTK solution<br />
on ice. At the time periods t=0, t=60,<br />
t=120, t=180, t=240, t=300, t=360, t=420,<br />
and t=480 a tissue sample of the gut was<br />
fixed and stained with H&E. The tissue<br />
was analyzed by three independent observers<br />
and scored for tissue damage<br />
(0=no damage, 1=minor damage, 2=major<br />
damage, 3= loss of structure) of 1. integrity<br />
of the mucosa, 2. integrity of the basal<br />
membrane of the mucosa and 3. integrity<br />
of villy. The occurrence of the damage was