Protocols and Applications Guide (US Letter Size) - Promega
Protocols and Applications Guide (US Letter Size) - Promega
Protocols and Applications Guide (US Letter Size) - Promega
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
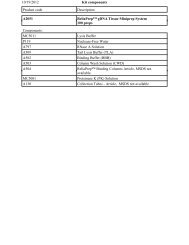
||||| 5Protein Expression<br />
mRNAs commonly exhibit different optimum salt<br />
concentrations for translation. Furthermore, small variations<br />
in salt concentration can lead to dramatic differences in<br />
translation efficiency. The Flexi® Rabbit Reticulocyte Lysate<br />
System allows optimization of a wide range of parameters,<br />
including Mg2+ <strong>and</strong> K+ concentrations, <strong>and</strong> offers the choice<br />
of adding DTT. To help optimize Mg2+ for a specific<br />
message, the endogenous Mg2+ concentration of each lysate<br />
batch is stated on the product insert. The Flexi® System<br />
also offers the choice of three amino acid mixtures <strong>and</strong><br />
includes a control RNA encoding the firefly luciferase gene.<br />
For a detailed protocol <strong>and</strong> background information about<br />
this system, please see Technical Bulletin #TB127<br />
(www.promega.com/tbs/tb127/tb127.html).<br />
Protocol<br />
Materials Required:<br />
• Flexi® Rabbit Reticulocyte Lysate System (Cat.# L4540)<br />
• RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor or RNasin® Plus RNase<br />
Inhibitor (Cat.# N2111 or N2611)<br />
• Nuclease-Free Water (Cat.# P1193)<br />
• radiolabeled amino acid (for radioactive detection) or<br />
Transcend tRNA (Cat.# L5061) or Transcend<br />
Colorimetric (Cat.# L5070) or Chemiluminescent (Cat.#<br />
L5080) Translation Detection System (for<br />
non-radioactive detection) or FluoroTect GreenLys in<br />
vitro Translation Labeling System (for fluorescent<br />
detection; Cat.# L5001)<br />
The following is a general guideline for setting up a Flexi®<br />
Lysate translation reaction. Also provided is an example<br />
of a st<strong>and</strong>ard reaction. The reaction uses [35S]methionine<br />
as the radiolabel; other isotopes may also be used (see Table<br />
5.3). For the positive control reaction, use 1–2µl of the<br />
Luciferase Control RNA supplied.<br />
1. Assemble the following reaction components in a 0.5ml<br />
or 1.5ml tube.<br />
Note: We recommend also including a negative control<br />
reaction containing no added template to allow<br />
measurement of background incorporation of labeled<br />
amino acids.<br />
Component<br />
Flexi® Rabbit Reticulocyte Lysate<br />
Amino Acid Mixture Minus<br />
Methionine, 1mM<br />
[35S]methionine (1,200Ci/mmol at<br />
10mCi/ml)<br />
Magnesium Acetate, 25mM<br />
Potassium Chloride, 2.5M<br />
DTT, 100mM<br />
RNasin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor<br />
(40u/ml)<br />
RNA substrate<br />
Nuclease-Free Water to final volume<br />
<strong>Protocols</strong> & <strong>Applications</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
www.promega.com<br />
rev. 6/09<br />
Volume<br />
33µl<br />
1µl<br />
2µl<br />
0–4µl<br />
1.4µl<br />
0–1µl<br />
1µl<br />
1–12µl<br />
50µl<br />
2. Incubate the translation reaction at 30°C for 60–90<br />
minutes.<br />
3. Analyze the results of translation.<br />
C. RNA Template Considerations<br />
Use a final concentration of 5–80µg/ml of in vitro transcripts<br />
produced with the RiboMAX Large Scale RNA<br />
Production Systems (Cat.# P1280 <strong>and</strong> P1300) for the<br />
translation. RNA from other st<strong>and</strong>ard transcription<br />
procedures may contain components at concentrations that<br />
inhibit translation. Therefore, a lower concentration,<br />
5–20µg/ml of in vitro transcript, should be used with these<br />
systems. The optimal RNA concentration should be<br />
determined before performing experiments. Average<br />
preparations of mRNA stimulate translation about 10- to<br />
20-fold over background (i.e., no exogenous RNA template).<br />
To determine the optimal concentration, serially dilute your<br />
RNA template first <strong>and</strong> then add the same volume of RNA<br />
to each reaction. This ensures that other variables are kept<br />
constant. In addition, the presence of certain nucleic acid<br />
sequence elements can have profound effects on initiation<br />
fidelity <strong>and</strong> translation efficiency; 3´-poly(A)+ sequences,<br />
5´-caps, 5´-untranslated regions <strong>and</strong> the sequence context<br />
around the AUG start, or secondary AUGs in the sequence<br />
(Kozak, 1990).<br />
The presence of inhibitors can significantly reduce<br />
translation efficiency. Oxidized thiols, low concentrations<br />
of double-str<strong>and</strong>ed RNA <strong>and</strong> polysaccharides are typical<br />
inhibitors of translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (Jackson<br />
<strong>and</strong> Hunt, 1983). To determine if inhibitors are present in<br />
your mRNA preparation, mix your RNA with Luciferase<br />
Control RNA <strong>and</strong> determine if translation of luciferase<br />
RNA is inhibited relative to a control translation containing<br />
only the luciferase RNA. Residual ethanol should also be<br />
removed from mRNA preparations <strong>and</strong> labeled amino<br />
acids before they are added to the translation reaction.<br />
You may need to optimize the potassium <strong>and</strong> magnesium<br />
concentrations in your translation reactions. Addition of<br />
0.5–2.5mM Mg2+ is generally sufficient for the majority of<br />
mRNAs. See Tables 5.4 <strong>and</strong> 5.5 for the concentrations of<br />
key components present in the lysate.<br />
Table 5.4. Final Concentrations of Rabbit Reticulocyte<br />
Lysate Components in a 50µl Translation Reaction.<br />
Final<br />
Components<br />
Concentration<br />
Creatine phosphate<br />
10mM<br />
Creatine phosphokinase<br />
50µg/ml<br />
DTT<br />
2mM<br />
Calf liver tRNA<br />
50µg/ml<br />
Potassium acetate<br />
79mM<br />
Magnesium acetate<br />
0.5mM<br />
Hemin<br />
0.02mM<br />
PROTOCOLS & APPLICATIONS GUIDE 5-9