Implementation of Metal Casting Best Practices - EERE - U.S. ...
Implementation of Metal Casting Best Practices - EERE - U.S. ...
Implementation of Metal Casting Best Practices - EERE - U.S. ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
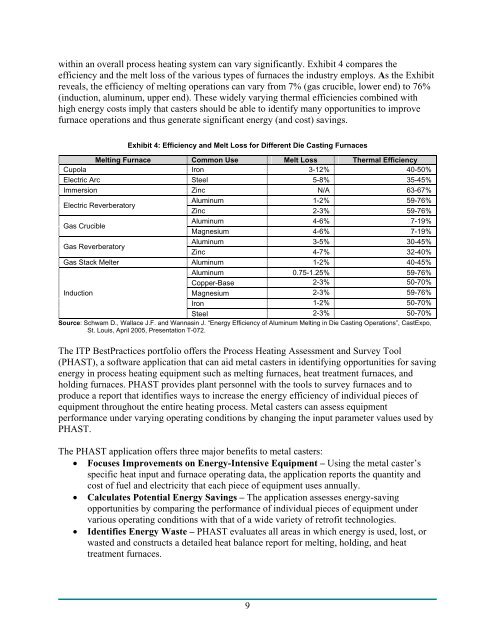
within an overall process heating system can vary significantly. Exhibit 4 compares the<br />
efficiency and the melt loss <strong>of</strong> the various types <strong>of</strong> furnaces the industry employs. As the Exhibit<br />
reveals, the efficiency <strong>of</strong> melting operations can vary from 7% (gas crucible, lower end) to 76%<br />
(induction, aluminum, upper end). These widely varying thermal efficiencies combined with<br />
high energy costs imply that casters should be able to identify many opportunities to improve<br />
furnace operations and thus generate significant energy (and cost) savings.<br />
Exhibit 4: Efficiency and Melt Loss for Different Die <strong>Casting</strong> Furnaces<br />
Melting Furnace Common Use Melt Loss Thermal Efficiency<br />
Cupola Iron 3-12% 40-50%<br />
Electric Arc Steel 5-8% 35-45%<br />
Immersion Zinc N/A 63-67%<br />
Electric Reverberatory<br />
Aluminum<br />
Zinc<br />
1-2%<br />
2-3%<br />
59-76%<br />
59-76%<br />
Gas Crucible<br />
Aluminum<br />
Magnesium<br />
4-6%<br />
4-6%<br />
7-19%<br />
7-19%<br />
Gas Reverberatory<br />
Aluminum<br />
Zinc<br />
3-5%<br />
4-7%<br />
30-45%<br />
32-40%<br />
Gas Stack Melter Aluminum 1-2% 40-45%<br />
Aluminum 0.75-1.25% 59-76%<br />
Copper-Base 2-3% 50-70%<br />
Induction<br />
Magnesium 2-3% 59-76%<br />
Iron 1-2% 50-70%<br />
Steel 2-3% 50-70%<br />
Source: Schwam D., Wallace J.F. and Wannasin J. “Energy Efficiency <strong>of</strong> Aluminum Melting in Die <strong>Casting</strong> Operations”, CastExpo,<br />
St. Louis, April 2005, Presentation T-072.<br />
The ITP <strong>Best</strong><strong>Practices</strong> portfolio <strong>of</strong>fers the Process Heating Assessment and Survey Tool<br />
(PHAST), a s<strong>of</strong>tware application that can aid metal casters in identifying opportunities for saving<br />
energy in process heating equipment such as melting furnaces, heat treatment furnaces, and<br />
holding furnaces. PHAST provides plant personnel with the tools to survey furnaces and to<br />
produce a report that identifies ways to increase the energy efficiency <strong>of</strong> individual pieces <strong>of</strong><br />
equipment throughout the entire heating process. <strong>Metal</strong> casters can assess equipment<br />
performance under varying operating conditions by changing the input parameter values used by<br />
PHAST.<br />
The PHAST application <strong>of</strong>fers three major benefits to metal casters:<br />
• Focuses Improvements on Energy-Intensive Equipment – Using the metal caster’s<br />
specific heat input and furnace operating data, the application reports the quantity and<br />
cost <strong>of</strong> fuel and electricity that each piece <strong>of</strong> equipment uses annually.<br />
• Calculates Potential Energy Savings – The application assesses energy-saving<br />
opportunities by comparing the performance <strong>of</strong> individual pieces <strong>of</strong> equipment under<br />
various operating conditions with that <strong>of</strong> a wide variety <strong>of</strong> retr<strong>of</strong>it technologies.<br />
• Identifies Energy Waste – PHAST evaluates all areas in which energy is used, lost, or<br />
wasted and constructs a detailed heat balance report for melting, holding, and heat<br />
treatment furnaces.<br />
9