Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines
Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines
Automotive spark-ignited direct-injection gasoline engines
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
540<br />
F. Zhao et al. / Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 25 (1999) 437–562<br />
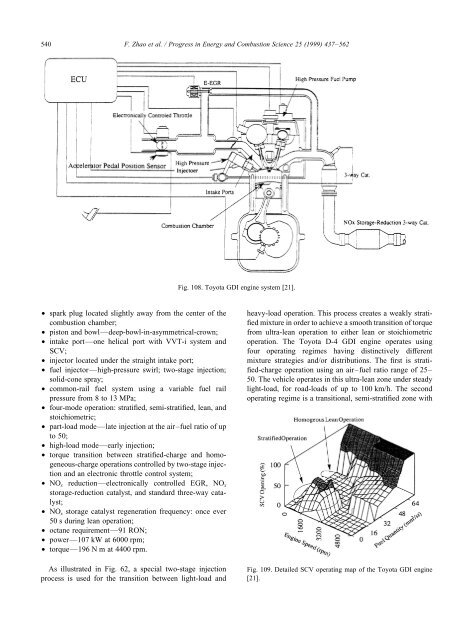
• <strong>spark</strong> plug located slightly away from the center of the<br />
combustion chamber;<br />
• piston and bowl—deep-bowl-in-asymmetrical-crown;<br />
• intake port—one helical port with VVT-i system and<br />
SCV;<br />
• injector located under the straight intake port;<br />
• fuel injector—high-pressure swirl; two-stage <strong>injection</strong>;<br />
solid-cone spray;<br />
• common-rail fuel system using a variable fuel rail<br />
pressure from 8 to 13 MPa;<br />
• four-mode operation: stratified, semi-stratified, lean, and<br />
stoichiometric;<br />
• part-load mode—late <strong>injection</strong> at the air–fuel ratio of up<br />
to 50;<br />
• high-load mode—early <strong>injection</strong>;<br />
• torque transition between stratified-charge and homogeneous-charge<br />
operations controlled by two-stage <strong>injection</strong><br />
and an electronic throttle control system;<br />
• NOx reduction—electronically controlled EGR, NOx<br />
storage-reduction catalyst, and standard three-way catalyst;<br />
• NO x storage catalyst regeneration frequency: once ever<br />
50 s during lean operation;<br />
• octane requirement—91 RON;<br />
• power—107 kW at 6000 rpm;<br />
• torque—196 N m at 4400 rpm.<br />
As illustrated in Fig. 62, a special two-stage <strong>injection</strong><br />
process is used for the transition between light-load and<br />
Fig. 108. Toyota GDI engine system [21].<br />
heavy-load operation. This process creates a weakly stratified<br />
mixture in order to achieve a smooth transition of torque<br />
from ultra-lean operation to either lean or stoichiometric<br />
operation. The Toyota D-4 GDI engine operates using<br />
four operating regimes having distinctively different<br />
mixture strategies and/or distributions. The first is stratified-charge<br />
operation using an air–fuel ratio range of 25–<br />
50. The vehicle operates in this ultra-lean zone under steady<br />
light-load, for road-loads of up to 100 km/h. The second<br />
operating regime is a transitional, semi-stratified zone with<br />
Fig. 109. Detailed SCV operating map of the Toyota GDI engine<br />
[21].