English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
38<br />
COUNTRY STUDY FOR BIODIVERSITY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA<br />
Angiosperms (Shopova 1966). This research has gradually become more intensive<br />
and comprehensive, involving a larger number of domestic and foreign researchers.<br />
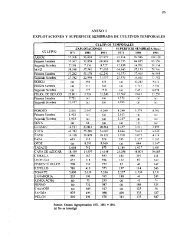
• The vegetati<strong>on</strong> diversity of higher plant groups is represented by 30 vegetati<strong>on</strong><br />
classes, 60 orders, 90 alliances and over 260 associati<strong>on</strong>s. The aquatic macrophytes<br />
(class Lemnetea and class Potametea), which are found in the three natural lakes of<br />
the country, are very well studied. Also well studied is the lowland marsh vegetati<strong>on</strong><br />
(class Isoeto-Nanojuncetea and class Phragmitetea), whereas there is little data<br />
about wetland vegetati<strong>on</strong> located in mountain marshes. Lowland meadows (class<br />
Molinio-Arrhenatheretea) are relatively well studied; however, meadows from the<br />
mountain to the subalpine belt are insufficiently studied. Halophytic vegetati<strong>on</strong><br />
(class Thero-Salicornietea) can be found <strong>on</strong> small areas and is completely studied,<br />
while the vegetati<strong>on</strong> of hilly pastures (class Festuco-Brometea) is in a phase of<br />
intensive research. Plant communities present <strong>on</strong> silicate soils are better studied than<br />
those found <strong>on</strong> carb<strong>on</strong>ate soils. The forest and shrub vegetati<strong>on</strong> is quite rich and<br />
diverse, and is represented by 100 associati<strong>on</strong>s. Some of them should be revised and<br />
harm<strong>on</strong>ised with the Internati<strong>on</strong>al Code <strong>on</strong> Phytocenological Nomenclature. The<br />
mountain and high mountain vegetati<strong>on</strong> is not sufficiently studied and the existing<br />
data is out of date. Because of this, some revisi<strong>on</strong>s and new research are necessary.<br />
With regard to the extent of study of individual faunal groups, from a tax<strong>on</strong>omic<br />
standpoint the well-studied phyla include: Porifera (sp<strong>on</strong>ges), Plathelminthes<br />
(flatworms), Mollusca (Molluscs), Annelida (segmented worms) and Chordata<br />
(Chordates). The study of the Chordates is complete. C<strong>on</strong>cerning the phylum Protozoa<br />
(Protozoans), the free living Protozoans are well studied; however, <strong>on</strong>ly representatives<br />
of the subphylum Ciliophora (Ciliated protozoans) have been studied from the parasitic<br />
Protozoan forms. As for the phylum Nemathelminthes (roundworms), the class Rotifera<br />
(Rotifers) is well studied, while of the class Nematoda, the aquatic free-living<br />
Nematodes and parasitic Nematodes are more completely studied. Terrestrial Nematodes<br />
have been studied <strong>on</strong>ly fragmentarily.<br />
Within the phylum Arthropoda (Arthropods), which has numerous species, the<br />
subphyla Branchiata (Branchiate arthropods) and Chelicerata (Chelicerates) are fully<br />
studied. The class Myriapoda (Myriapods) of the subphylum Tracheata (Tracheates) is<br />
well studied, unlike the class Insecta (Insects), where complete data exist <strong>on</strong>ly for the<br />
orders Ephemeroptera (Mayflies), Lepidoptera (butterflies), Od<strong>on</strong>ata (drag<strong>on</strong>flies),<br />
Orthoptera (grasshoppers) and Plecoptera (st<strong>on</strong>eflies). The other orders of this class,<br />
with their numerous families, genera and species, are <strong>on</strong>ly fragmentarily studied or have<br />
never been subject to any systematic study.<br />
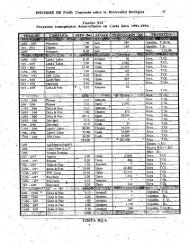
Currently, as in the past, the primary areas of research into Maced<strong>on</strong>ian faunal<br />
biodiversity are the ecosystems of the three natural lakes, which abound in limnofauna,<br />
as well as the other fauna inhabiting the lake basins. In additi<strong>on</strong>, the fauna of hilly<br />
pastures and lowlands, and that of mountain ecosystems, has been well explored, while<br />
the fauna of forest ecosystems has rarely been studied.<br />
3.2. Biogeography<br />
The great floristic and faunal diversity of the Republic of Maced<strong>on</strong>ia can be<br />
explained due to its central geographical positi<strong>on</strong> in the Balkan Peninsula and the<br />
various influences to which its territory has been exposed. The fluctuati<strong>on</strong>s of<br />
temperatures before, during and after the Ice Age caused multiple, dramatic migrati<strong>on</strong>s