English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
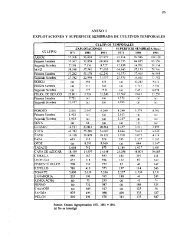
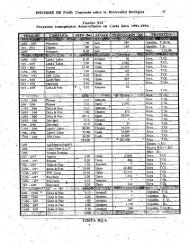
COUNTRY STUDY FOR BIODIVERSITY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA<br />
3.6.6. Climate change<br />
On the basis of an evaluati<strong>on</strong> of the impacts of climatic changes <strong>on</strong> biodiversity, the<br />
future horiz<strong>on</strong>tal and vertical distributi<strong>on</strong> of plant and animal species are expected to<br />
change, (i.e., migrati<strong>on</strong> toward the north and/or migrati<strong>on</strong> to higher elevati<strong>on</strong>s). Such<br />
changes will particularly affect the relict plant and animal species living in high<br />
mountain z<strong>on</strong>es.<br />
According to the results presented by the MoEPP in the First Nati<strong>on</strong>al Report <strong>on</strong><br />
Climate Changes, the areas most sensitive to climatic changes are the refugial z<strong>on</strong>es:<br />
Taor Gorge; Treska River gorge; Crna River, including the gorges of the Raets and<br />
Blashnitsa Rivers; Jama; Mavrovo-Radika; Pelister; Ohrid-Prespa and Nidze-Kozhuf.<br />
Within these z<strong>on</strong>es, many refugial phytocenoses are present which would be endangered<br />
by temperature increases and by the accompanying decreases or distributi<strong>on</strong>al changes<br />
in precipitati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
With an increase in temperature of 3.2ºC (IS92a model) over the next 100 years,<br />
even the highest peaks would suffer higher mean annual temperatures <strong>on</strong> a par with the<br />
current temperatures in the higher subalpine z<strong>on</strong>es (i.e., the z<strong>on</strong>es of species distributi<strong>on</strong><br />
would migrate upward by 500 m), so that alpine pastures would be expected to disappear<br />
completely <strong>on</strong> some mountains.<br />
In c<strong>on</strong>trast to the alpine pastures, the thermophilic communities, such as the<br />
pseudomaquis (a type of Mediterranian shrubland), would expand their ranges into<br />
northern regi<strong>on</strong>s and higher altitudes. New thermophilic communities would be expected<br />
to appear, such as Mediterranean grass communities. Other climate-z<strong>on</strong>al communities<br />
would experience changes in their areal and elevati<strong>on</strong>al distributi<strong>on</strong>s, depending <strong>on</strong> the<br />
rate of advancement of the climatic changes.<br />
3.6.7. Natural Disasters<br />
Natural disasters do occur, but <strong>on</strong>ly infrequently and of minor intensity. Maced<strong>on</strong>ia<br />
is a seismic area, however, and a large part of its territory is arid and semiarid and there<br />
are frequent landslides, avalanches etc.<br />
Droughts are frequent natural disasters. In additi<strong>on</strong> to the droughts of short durati<strong>on</strong><br />
which are characteristic for a major porti<strong>on</strong> of the country, there are also extended<br />
periodic droughts, which cause great ec<strong>on</strong>omic hardships for agriculture, as well as<br />
serious damage to the natural inland mesophilic ecosystems. Examples of this include<br />
reducti<strong>on</strong> in the growth rates of forests, defoliati<strong>on</strong> and increased susceptibility to<br />
parasites and other pests, the desiccati<strong>on</strong> of marsh ecosystems, disturbances to the<br />
hydrology of aquatic ecosystems (Doyran and Prespa lakes) etc.<br />
Forest fires are usually caused by human activities; however, due to their<br />
dramatically increased frequency during periods of drought, they can be listed as natural<br />
disasters. They are frequent in the sub-Mediterranean and hot c<strong>on</strong>tinental areas, where<br />
communities of scrub forests and Hornbeam important from the aspect of biodiversity<br />
develop.<br />
Landslides are frequent occurrances, but take place in a much more localised area<br />
than drought or fire. These are phenomena where milli<strong>on</strong>s of cubic metres of soil begin<br />
to suddenly move, destroying large agricultural areas (Kavadartsi) and forests (Dolna<br />
River near the village of Bitushe). In the area of Kavadartsi (near the village of Vatasha),<br />
a large landslide thirty years ago closed the gorge of the Luda Mara River, forming a<br />
reservoir which is currently being used for irrigati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
73