English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
80<br />
COUNTRY STUDY FOR BIODIVERSITY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA<br />
do indicate an alarming situati<strong>on</strong>, dem<strong>on</strong>strated in the maximum annual quantities of<br />
medicinal plant material exported in the last decade: Altahea officinalis (80 t<strong>on</strong>nes),<br />
Chamomilla recutita (75 t<strong>on</strong>nes), Gentina lutea and G. punctata (3-4 t<strong>on</strong>nes), Hypericum<br />
perforatum (5,000 t<strong>on</strong>nes), Lichenes (1,200 t<strong>on</strong>nes) and Tilia cordata (60 t<strong>on</strong>nes).<br />
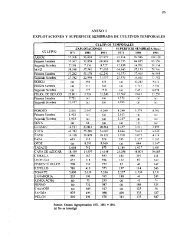
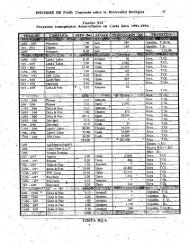
Annex 6, Table 6 lists the medicinal plant species used in Maced<strong>on</strong>ia. The collecti<strong>on</strong><br />
and use of medicinal plants can be divided into three categories: pers<strong>on</strong>al use,<br />
retail/wholesale trade and other ec<strong>on</strong>omic purposes. A mechanism for regulati<strong>on</strong> and<br />
classificati<strong>on</strong> is necessary before it can be determined how much dry plant material an<br />
individual can collect from an area and before a permit for this collecti<strong>on</strong> can be issued.<br />
The collecti<strong>on</strong> of medicinal plants for ec<strong>on</strong>omic purposes in Maced<strong>on</strong>ia varies<br />
widely with the species collected, the collectors themselves and the seas<strong>on</strong>al quantity of<br />
the collected material. Most serious is the large seas<strong>on</strong>al demand by foreign buyers for<br />
specific plant species, facilitated by certain local trade companies which have no<br />
previous experience in this field. According to the nature of the plant material used (e.g.,<br />
root, fruit, leaf, flower or stem), the greatest risks and threats are for those plants which<br />
are used whole, followed by those whose roots are collected and then those with useful<br />
bark. Species with a restricted area of distributi<strong>on</strong> are most threatened (e.g., Acorus<br />
calamus, Salvia officinalis and Sideritis scardica). Based <strong>on</strong> data from the past ten years,<br />
the most troubling situati<strong>on</strong>s are with the species: Ad<strong>on</strong>is vernalis, Colchicum<br />
autumnale, Herniaria glabra, H. hirsuta, Gentiana lutea, G. punctata, Hypericum<br />
perforatum, Lichenes, various species within the genera of the family Orchidaceae,<br />
whose parts are used in the producti<strong>on</strong> of salep, Sideritis scardica, S. raeserii and<br />
Thymus spp.<br />
4.2.1.5. Other uses, including species used in foreign trade<br />
Wild species are sometimes used in the cosmetics, alcohol and c<strong>on</strong>structi<strong>on</strong><br />
industries. Lichens and mosses, used in the cosmetics industry, are collected in the<br />
eastern and western mountains of Maced<strong>on</strong>ia and then exported (the annual purchase<br />
reaches 600-800 t<strong>on</strong>nes dry weight; the exported amount in 2001 was 83,334 kg, valued<br />
at $79,624). Essential oils are extracted from c<strong>on</strong>es, needles or seeds of Pine and other<br />
plant species. For the producti<strong>on</strong> of gin, the alcohol industry uses the berries (mainly the<br />
blue <strong>on</strong>es) of the juniper bush. The exported amount in 2001 was 991,067 kg, valued at<br />
$758,463. The annual purchase of juniper berries by various organisati<strong>on</strong>s is 3-4,000<br />
t<strong>on</strong>nes. Reeds, Cattails and Willows are used in c<strong>on</strong>structi<strong>on</strong>, either dried, woven, as<br />
thatch or in handicraft products. They are mainly collected <strong>on</strong> the lakes (Ohrid, Prespa,<br />
Doyran), however this activity is <strong>on</strong> the decline.<br />
4.2.2. Use of wild animals<br />
4.2.2.1. Hunting<br />
Hunting is c<strong>on</strong>ducted through hunting associati<strong>on</strong>s combined under the Hunting<br />
Uni<strong>on</strong> of Maced<strong>on</strong>ia. The largest porti<strong>on</strong> of the land licensed for hunting c<strong>on</strong>sists of<br />
forests and forested areas. Protective measures for the care of forests and of game often<br />
do not agree. There is a need to coordinate these measures within the two sectors.