English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
English - Convention on Biological Diversity
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
COUNTRY STUDY FOR BIODIVERSITY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA<br />
4. USE AND VALUES OF BIODIVERSITY<br />
4.1. Agrobiodiversity<br />
<strong>Biological</strong> diversity in agriculture is <strong>on</strong>e of the most critical areas of the overall<br />
biodiversity <strong>on</strong> the globe, with 75% of all food producti<strong>on</strong> based up<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong>ly about 100<br />
plant species and domestic animals. As civilisati<strong>on</strong>s developed, humans strove to create<br />
plant varieties and domestic animals with more useful traits, which c<strong>on</strong>tributed to an<br />
increase in the diversity of the genetic resources of the various species. By crossing<br />
various genetic materials, humans began the practical creati<strong>on</strong> of varieties and breeds.<br />
This process has been occurring for at least the past 50-100 years and c<strong>on</strong>tinues even<br />
now. Today, however, under the pressure of increased profitability, far more specialised<br />
genotypes characterised by the term, “high input – high output,” are being promoted. At<br />
the same time, traditi<strong>on</strong>al breeding using natural species is often neglected, although it<br />
often offers the best soluti<strong>on</strong>s for the existing c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s in a given envir<strong>on</strong>ment. As a<br />
result of this tendency, many varieties and breeds have not been able to endure under<br />
this modern capitalistic <strong>on</strong>slaught and have been lost as genetic resources. This trend is<br />
still c<strong>on</strong>tinuing, and there are estimates which show that, worldwide, about 30% of<br />
domestic animal breeds have permanently disappeared.<br />
In the Republic of Maced<strong>on</strong>ia, biological resources represented by indigenous<br />
varieties, breeds and species should be preserved for the sake of ec<strong>on</strong>omic, scientific,<br />
cultural, socioec<strong>on</strong>omic and envir<strong>on</strong>mental interests.<br />
4.1.1. Crops<br />
Maced<strong>on</strong>ia possesses significant agrobiological plant diversity due to its favourable<br />
geographic locati<strong>on</strong> and climatic c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s. The diversity of a large porti<strong>on</strong> of the local<br />
species has not been adversely affected because agricultural producti<strong>on</strong> is not intensive<br />
in many regi<strong>on</strong>s. In such areas, indigenous species and locally-bred varieties are grown,<br />
representing an important source of genetic material no l<strong>on</strong>ger appearing within the<br />
genotype of commercial species.<br />
The major porti<strong>on</strong> of the total arable land is used for field and garden producti<strong>on</strong><br />
(84.2%), with the greatest percentage c<strong>on</strong>sisting of wheat, tomatoes and peppers. Fruit<br />
and grape producti<strong>on</strong> comprises 7.1 %, mostly c<strong>on</strong>sisting of native and introduced<br />
grapes (4.4 %), apples and plums. Meadows cover 8.5%, and are most often planted with<br />
alfalfa. The breakdown of grain crops, vegetables and fodder crops is presented in<br />
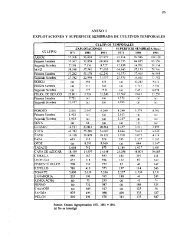
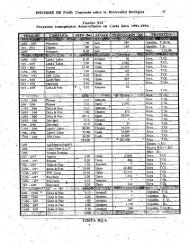
Annex 6, Table1, whereas that of fruit producti<strong>on</strong> in Annex 6, Table 2.<br />
The trends in the producti<strong>on</strong> of individual crops vary by year, as evidenced by the<br />
disappearance of some crops (e.g., poppy, flax, hemp and cott<strong>on</strong>), reducing the diversity<br />
of species cultivated. On the c<strong>on</strong>trary, cucurbit crops, which appear in great diversity but<br />
are not c<strong>on</strong>sidered an important part of agricultural producti<strong>on</strong>, are expected to cover<br />
about 2,000 ha in 2005.<br />
The bulk of the crops produced c<strong>on</strong>sist of commercial varieties, the major porti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
which are imported from abroad, with a minor number of locally-developed varieties,<br />
mainly created by the Institute of Agriculture in Skopye. Small producers still grow local<br />
varieties and indigenous species, especially in garden plant producti<strong>on</strong>. The number of<br />
varieties/species used in agricultural producti<strong>on</strong> within Maced<strong>on</strong>ia is evidence of great<br />
biological diversity. There are 129 recognised domestic varieties and 2,205 imported<br />
varieties used domestically. A detailed review of the number of varieties by crop is<br />
presented in Annex 6, Table 3.<br />
75