Strona 2_redak - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego ...
Strona 2_redak - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego ...
Strona 2_redak - Instytut Agrofizyki im. Bohdana DobrzaÅskiego ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
51<br />
N=σ r<br />
πD 2<br />
4<br />
T = τ πD 2<br />
4<br />
ro u g h<br />
H<br />
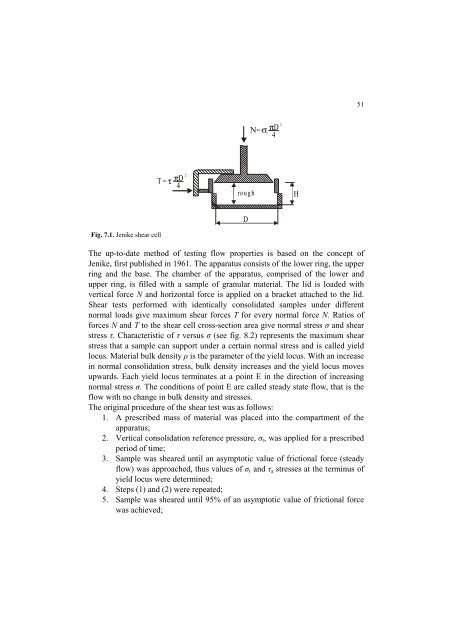
Fig. 7.1. Jenike shear cell<br />
D<br />
The up-to-date method of testing flow properties is based on the concept of<br />
Jenike, first published in 1961. The apparatus consists of the lower ring, the upper<br />
ring and the base. The chamber of the apparatus, comprised of the lower and<br />
upper ring, is filled with a sample of granular material. The lid is loaded with<br />
vertical force N and horizontal force is applied on a bracket attached to the lid.<br />
Shear tests performed with identically consolidated samples under different<br />
normal loads give max<strong>im</strong>um shear forces T for every normal force N. Ratios of<br />
forces N and T to the shear cell cross-section area give normal stress σ and shear<br />
stress τ. Characteristic of τ versus σ (see fig. 8.2) represents the max<strong>im</strong>um shear<br />
stress that a sample can support under a certain normal stress and is called yield<br />
locus. Material bulk density ρ is the parameter of the yield locus. With an increase<br />
in normal consolidation stress, bulk density increases and the yield locus moves<br />
upwards. Each yield locus terminates at a point E in the direction of increasing<br />
normal stress σ. The conditions of point E are called steady state flow, that is the<br />
flow with no change in bulk density and stresses.<br />
The original procedure of the shear test was as follows:<br />
1. A prescribed mass of material was placed into the compartment of the<br />
apparatus;<br />
2. Vertical consolidation reference pressure, σ r , was applied for a prescribed<br />
period of t<strong>im</strong>e;<br />
3. Sample was sheared until an asymptotic value of frictional force (steady<br />
flow) was approached, thus values of σ r and τ a stresses at the terminus of<br />
yield locus were determined;<br />
4. Steps (1) and (2) were repeated;<br />
5. Sample was sheared until 95% of an asymptotic value of frictional force<br />
was achieved;