TSUBAKI EMERSON CAM CLUTCH
TSUBAKI EMERSON CAM CLUTCH
TSUBAKI EMERSON CAM CLUTCH
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
www.bergab.ru Берг АБ bergab@ya.ru Тел. (495)-228-06-21, факс (495) 223-3071<br />
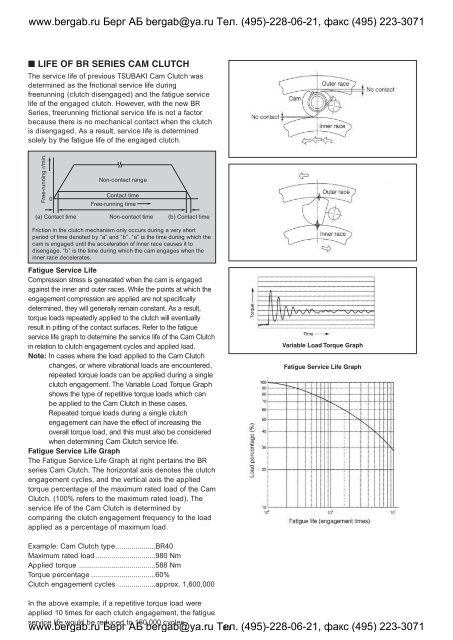
■ LIFE OF BR SERIES <strong>CAM</strong> <strong>CLUTCH</strong><br />
The service life of previous <strong>TSUBAKI</strong> Cam Clutch was<br />
determined as the frictional service life during<br />
freerunning (clutch disengaged) and the fatigue service<br />
life of the engaged clutch. However, with the new BR<br />
Series, freerunning frictional service life is not a factor<br />
because there is no mechanical contact when the clutch<br />
is disengaged. As a result, service life is determined<br />
solely by the fatigue life of the engaged clutch.<br />
Free-running r/min.<br />
0<br />
Non-contact range<br />
Contact time<br />
Free-running time<br />
(a) Contact time<br />
Non-contact time<br />
(b) Contact time<br />
Friction in the clutch mechanism only occurs during a very short<br />
period of time denoted by “a” and “b”. “a” is the time during which the<br />
cam is engaged until the acceleration of inner race causes it to<br />
disengage. “b” is the time during which the cam engages when the<br />
inner race decelerates.<br />
Fatigue Service Life<br />
Compression stress is generated when the cam is engaged<br />
against the inner and outer races. While the points at which the<br />
engagement compression are applied are not specifically<br />
determined, they will generally remain constant. As a result,<br />
torque loads repeatedly applied to the clutch will eventually<br />
result in pitting of the contact surfaces. Refer to the fatigue<br />
service life graph to determine the service life of the Cam Clutch<br />
in relation to clutch engagement cycles and applied load.<br />
Note: In cases where the load applied to the Cam Clutch<br />
changes, or where vibrational loads are encountered,<br />
repeated torque loads can be applied during a single<br />
clutch engagement. The Variable Load Torque Graph<br />
shows the type of repetitive torque loads which can<br />
be applied to the Cam Clutch in these cases.<br />
Repeated torque loads during a single clutch<br />
engagement can have the effect of increasing the<br />
overall torque load, and this must also be considered<br />
when determining Cam Clutch service life.<br />
Fatigue Service Life Graph<br />
The Fatigue Service Life Graph at right pertains the BR<br />
series Cam Clutch. The horizontal axis denotes the clutch<br />
engagement cycles, and the vertical axis the applied<br />
torque percentage of the maximum rated load of the Cam<br />
Clutch. (100% refers to the maximum rated load). The<br />
service life of the Cam Clutch is determined by<br />
comparing the clutch engagement frequency to the load<br />
applied as a percentage of maximum load.<br />
Variable Load Torque Graph<br />
Fatigue Service Life Graph<br />
Example: Cam Clutch type....................BR40<br />
Maximum rated load..............................980 Nm<br />
Applied torque ......................................588 Nm<br />
Torque percentage ................................60%<br />
Clutch engagement cycles ..................approx. 1,600,000<br />
In the above example, if a repetitive torque load were<br />
applied 10 times for each clutch engagement, the fatigue<br />
service life would reduced to 160,000 cycles.<br />
www.bergab.ru Берг АБ bergab@ya.ru Тел. 83 (495)-228-06-21, факс (495) 223-3071