as at December 31, 2003 - EFG Bank Group
as at December 31, 2003 - EFG Bank Group
as at December 31, 2003 - EFG Bank Group
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
30<br />
Notes to the Consolid<strong>at</strong>ed Financial St<strong>at</strong>ements (continued)<br />
19. Deriv<strong>at</strong>ive financial instruments<br />
The <strong>Group</strong> utilises the following deriv<strong>at</strong>ive instruments for both hedging and non-hedging purposes:<br />
Currency forwards represent commitments to purch<strong>as</strong>e or sell foreign and domestic currency. Foreign currency and<br />
interest r<strong>at</strong>e futures are contractual oblig<strong>at</strong>ions to receive or pay a net amount b<strong>as</strong>ed on changes in currency r<strong>at</strong>es or<br />
interest r<strong>at</strong>es, or buy or sell foreign currency or a financial instrument on a future d<strong>at</strong>e, <strong>at</strong> a specified price, established<br />
in an organised financial market. Since future contracts are coll<strong>at</strong>eralised by c<strong>as</strong>h or marketable securities and changes<br />
in the futures contract value are settled daily with the exchange, the credit risk is negligible.<br />
Currency and interest r<strong>at</strong>e swaps are commitments to exchange one set of c<strong>as</strong>h flows for another. Swaps result in an<br />
economic exchange of currencies or interest r<strong>at</strong>es (for example, fixed r<strong>at</strong>e for flo<strong>at</strong>ing r<strong>at</strong>e) or a combin<strong>at</strong>ion of all<br />
these (i.e. cross-currency interest r<strong>at</strong>e swaps). Except for certain currency swaps, no exchange of principal takes place.<br />
The <strong>Group</strong>’s credit risk represents the potential cost to replace the swap contracts if counterparties fail to perform<br />
their oblig<strong>at</strong>ion. This risk is monitored on an ongoing b<strong>as</strong>is with reference to the current fair value, a proportion of<br />
the notional amount of the contracts and the liquidity of the market. To control the level of credit risk taken, the<br />
<strong>Group</strong> <strong>as</strong>sesses counterparties using the same techniques <strong>as</strong> for its lending activities - and/or marks to market with<br />
bil<strong>at</strong>eral coll<strong>at</strong>eralis<strong>at</strong>ion agreements over and above an agreed threshold.<br />
Foreign currency and interest r<strong>at</strong>e options are contractual agreements under which the seller (writer) grants the<br />
purch<strong>as</strong>er (holder) the right, but not the oblig<strong>at</strong>ion, either to buy (a call option) or sell (a put option) <strong>at</strong> or by a set<br />
d<strong>at</strong>e or during a set period, a specific amount of a foreign currency or a financial instrument <strong>at</strong> a predetermined price.<br />
In consider<strong>at</strong>ion for the <strong>as</strong>sumption of foreign exchange or interest r<strong>at</strong>e risk, the seller receives a premium from the<br />
purch<strong>as</strong>er. Options may be either exchange-traded or negoti<strong>at</strong>ed between the <strong>Group</strong> and a customer (OTC). The<br />
<strong>Group</strong> is exposed to credit risk on purch<strong>as</strong>ed options only, and only to the extent of their carrying amount, which is<br />
their fair value.<br />
The notional amounts of certain types of financial instruments provide a b<strong>as</strong>is for comparison with instruments<br />
recognised on the balance sheet but do not necessarily indic<strong>at</strong>e the amounts of future c<strong>as</strong>h flows involved or the<br />
current fair value of the instruments and, therefore, do not indic<strong>at</strong>e the <strong>Group</strong>’s exposure to credit or price risks. The<br />
deriv<strong>at</strong>ive instruments become favourable (<strong>as</strong>sets) or unfavourable (liabilities) <strong>as</strong> a result of fluctu<strong>at</strong>ions in market<br />
interest r<strong>at</strong>es or foreign exchange r<strong>at</strong>es rel<strong>at</strong>ive to their terms. The aggreg<strong>at</strong>e contractual or notional amount of<br />
deriv<strong>at</strong>ive financial instruments on hand, the extent to which instruments are favourable or unfavourable and, thus<br />
the aggreg<strong>at</strong>e fair values of deriv<strong>at</strong>ive financial <strong>as</strong>sets and liabilities can fluctu<strong>at</strong>e significantly from time to time. The<br />
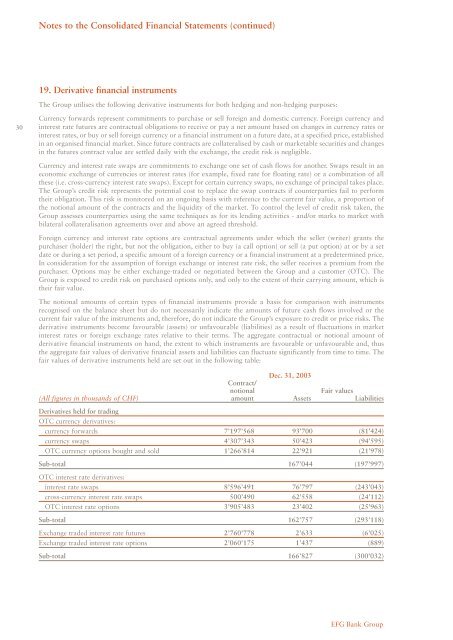
fair values of deriv<strong>at</strong>ive instruments held are set out in the following table:<br />
Dec. <strong>31</strong>, <strong>2003</strong><br />
Contract/<br />
notional Fair values<br />
(All figures in thousands of CHF) amount Assets Liabilities<br />
Deriv<strong>at</strong>ives held for trading<br />
OTC currency deriv<strong>at</strong>ives:<br />
currency forwards 7’197’568 93’700 (81’424)<br />
currency swaps 4’307’343 50’423 (94’595)<br />
OTC currency options bought and sold 1’266’814 22’921 (21’978)<br />
Sub-total 167’044 (197’997)<br />
OTC interest r<strong>at</strong>e deriv<strong>at</strong>ives:<br />
interest r<strong>at</strong>e swaps 8’596’491 76’797 (243’043)<br />
cross-currency interest r<strong>at</strong>e swaps 500’490 62’558 (24’112)<br />
OTC interest r<strong>at</strong>e options 3’905’483 23’402 (25’963)<br />
Sub-total 162’757 (293’118)<br />
Exchange traded interest r<strong>at</strong>e futures 2’760’778 2’633 (6’025)<br />
Exchange traded interest r<strong>at</strong>e options 2’060’175 1’437 (889)<br />
Sub-total 166’827 (300’032)<br />
<strong>EFG</strong> <strong>Bank</strong> <strong>Group</strong>