T 7.2.1.3 Amplitude Modulation
T 7.2.1.3 Amplitude Modulation
T 7.2.1.3 Amplitude Modulation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
TPS <strong>7.2.1.3</strong><br />
Double Sideband AM<br />
Compare the results. How does the USL respond<br />
as a function of the signal frequency f M ? What<br />
about the LSL? What is the frequency response of<br />
the LSL and USL? Determine the transmission<br />
bandwidth of the AM signal based on the measurements.<br />
Generalize your results for a randomly taken<br />
modulating signal. Determine the modulation<br />
depth m from the various spectra.<br />
5.2.2 DSB SC<br />
Set the toggle switch to CARRIER OFF. Use a<br />
sinusoidal signal with A M = 2 V and f M = 2 kHz as<br />
a modulating signal. Measure the spectrum as in<br />
point 5.2.1. Enter all your results in Table 5.2.2-1<br />
and Diagram 5.2.2-1.<br />
Table 5.2.2-1: DSB SC Spectrum<br />
Signal parameter<br />
Analyzer settings<br />
A C : V V 1 :<br />
f C : kHz b : Hz<br />
f r : kHz<br />
A M : V T : s<br />
f M : kHz<br />
s AM<br />
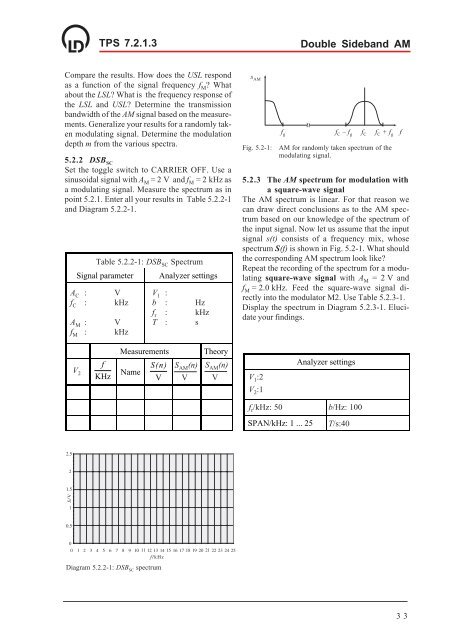
f g f C – f g f C f C + f g<br />
Fig. 5.2-1:<br />
AM for randomly taken spectrum of the<br />
modulating signal.<br />
5.2.3 The AM spectrum for modulation with<br />
a square-wave signal<br />
The AM spectrum is linear. For that reason we<br />
can draw direct conclusions as to the AM spectrum<br />
based on our knowledge of the spectrum of<br />
the input signal. Now let us assume that the input<br />
signal s(t) consists of a frequency mix, whose<br />
spectrum S(f) is shown in Fig. 5.2-1. What should<br />
the corresponding AM spectrum look like?<br />
Repeat the recording of the spectrum for a modulating<br />
square-wave signal with A M = 2 V and<br />
f M = 2.0 kHz. Feed the square-wave signal directly<br />
into the modulator M2. Use Table 5.2.3-1.<br />
Display the spectrum in Diagram 5.2.3-1. Elucidate<br />
your findings.<br />
f<br />
V 2<br />
f<br />
KHz<br />
Measurements<br />
S( n)<br />
Name<br />
V<br />
S AM (n)<br />
V<br />
Theory<br />
S AM (n)<br />
V<br />
V 1 :2<br />
V 2 :1<br />
Analyzer settings<br />
f r /kHz: 50 b/Hz: 100<br />
SPAN/kHz: 1 ... 25<br />
T/s:40<br />
Diagram 5.2.2-1: DSB SC<br />
spectrum<br />
33