Vol 44 # 2 June 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 2 June 2012 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 44 # 2 June 2012 - Kma.org.kw
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>June</strong> <strong>2012</strong><br />
KUWAIT MEDICAL JOURNAL 126<br />
showed no decrease in erythrocyte and hemoglobin<br />
values during the luteal phase [15] . Hunt and Penland [16]<br />
found that during the follicular phase, 4% of the<br />
women had reduced hemoglobin and 20% had<br />
decreased ferritin levels. Blood glucose consumption<br />
and carbohydrate oxidation have been shown to be<br />
reduced during the early luteal (EL) phase compared<br />
with the follicular phase [17] . Varying results have been<br />
obtained about the changes in hematologic parameters<br />
prior to menstruation (e.g., during the luteal phase)<br />
and after the menstruation (e.g., during the follicular<br />
phase), and those changes are attributed particularly<br />
to the influence of hormones such as estrogen and<br />
progesterone [18] . Determining the relationship between<br />
hematologic parameters and PMS may contribute to<br />
alleviation of the related symptoms. We conducted<br />
this study in order to evaluate the association between<br />
PMS and hematologic parameters during EF phase<br />
and late luteal (LL) phase.<br />
SUBJECTS AND METHOD<br />
Approval of the local ethics committee was<br />
taken prior to the beginning of the study. One<br />
hundred and eighteen healthy female volunteer<br />
students participated. The data were collected by<br />
questionnaires and PMS status was evaluated by the<br />
Premenstrual Syndrome Scale (PMSS) developed by<br />
Gencdogan in 2006 [19] . PMSS is a five-point (never: 1<br />
point; rarely: 2 points; sometimes: 3 points; very often:<br />
4 points; always: 5 points) Likert-type scale including<br />
<strong>44</strong> items and nine subdimensions. (Appendix 1).<br />
PMSS score above 110 points suggests the presence<br />
of PMS. There are nine subdimensions of this scale:<br />
depressive feeling, anxiety, fatigue, irritability,<br />
depressive thoughts, pain, changes in appetite,<br />
changes in sleeping habits, and swelling. Cronbach’s<br />
alpha coefficient is calculated as 0.959 for reliability<br />
of PMSS; for subscales the factor alpha ranged from<br />
0.933 and 0.991. We measured fasting blood glucose,<br />
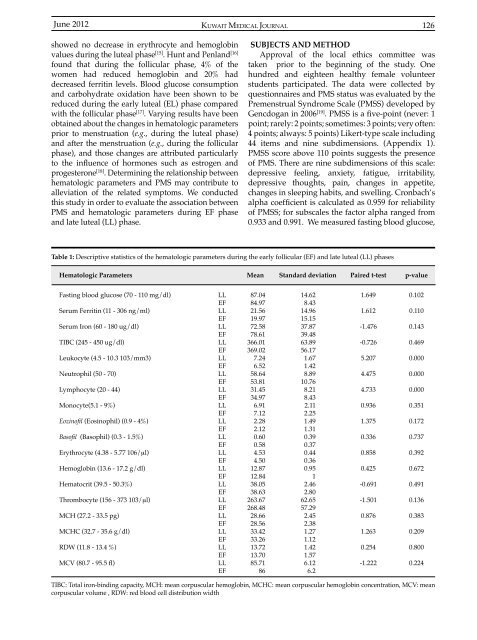
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of the hematologic parameters during the early follicular (EF) and late luteal (LL) phases<br />
Hematologic Parameters Mean Standard deviation Paired t-test p-value<br />
Fasting blood glucose (70 - 110 mg/dl)<br />
Serum Ferritin (11 - 306 ng/ml)<br />
Serum Iron (60 - 180 ug/dl)<br />
TIBC (245 - 450 ug/dl)<br />
Leukocyte (4.5 - 10.3 103/mm3)<br />
Neutrophil (50 - 70)<br />
Lymphocyte (20 - <strong>44</strong>)<br />
Monocyte(5.1 - 9%)<br />
Eozinofil (Eosinophil) (0.9 - 4%)<br />
Basofil (Basophil) (0.3 - 1.5%)<br />
Erythrocyte (4.38 - 5.77 106/μl)<br />
Hemoglobin (13.6 - 17.2 g/dl)<br />
Hematocrit (39.5 - 50.3%)<br />
Thrombocyte (156 - 373 103/μl)<br />
MCH (27.2 - 33.5 pg)<br />
MCHC (32.7 - 35.6 g/dl)<br />
RDW (11.8 - 13.4 %)<br />
MCV (80.7 - 95.5 fl)<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
LL<br />
EF<br />
87.04<br />
84.97<br />
21.56<br />
19.97<br />
72.58<br />
78.61<br />
366.01<br />
369.02<br />
7.24<br />
6.52<br />
58.64<br />
53.81<br />
31.45<br />
34.97<br />
6.91<br />
7.12<br />
2.28<br />
2.12<br />
0.60<br />
0.58<br />
4.53<br />
4.50<br />
12.87<br />
12.84<br />
38.05<br />
38.63<br />
263.67<br />
268.48<br />
28.66<br />
28.56<br />
33.42<br />
33.26<br />
13.72<br />
13.70<br />
85.71<br />
86<br />
14.62<br />
8.43<br />
14.96<br />
15.15<br />
37.87<br />
39.48<br />
63.89<br />
56.17<br />
1.67<br />
1.42<br />
8.89<br />
10.76<br />
8.21<br />
8.43<br />
2.11<br />
2.25<br />
1.49<br />
1.31<br />
0.39<br />
0.37<br />
0.<strong>44</strong><br />
0.36<br />
0.95<br />
1<br />
2.46<br />
2.80<br />
62.65<br />
57.29<br />
2.45<br />
2.38<br />
1.27<br />
1.12<br />
1.42<br />
1.57<br />
6.12<br />
6.2<br />
1.649<br />
1.612<br />
-1.476<br />
-0.726<br />
5.207<br />
4.475<br />
4.733<br />
0.936<br />
1.375<br />
0.336<br />
0.858<br />
0.425<br />
-0.691<br />
-1.501<br />
0.876<br />
1.263<br />
0.254<br />
-1.222<br />
0.102<br />
0.110<br />
0.143<br />
0.469<br />
0.000<br />
0.000<br />
0.000<br />
0.351<br />
0.172<br />
0.737<br />
0.392<br />
0.672<br />
0.491<br />
0.136<br />
0.383<br />
0.209<br />
0.800<br />
0.224<br />
TIBC: Total iron-binding capacity, MCH: mean corpuscular hemoglobin, MCHC: mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, MCV: mean<br />
corpuscular volume , RDW: red blood cell distribution width