Stylistic 1200 Tech Reference Manual (PDF) - The Labs
Stylistic 1200 Tech Reference Manual (PDF) - The Labs
Stylistic 1200 Tech Reference Manual (PDF) - The Labs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
an interrupt, the system returns to the Fully On state until all pending instructions are executed. If the<br />
Idle Mode option is disabled in the BIOS, the system will not enter Idle mode.<br />
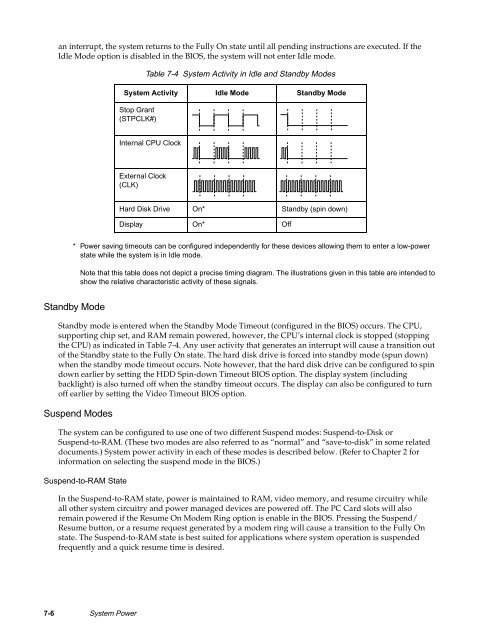
Table 7-4 System Activity in Idle and Standby Modes<br />
System Activity Idle Mode Standby Mode<br />
Stop Grant<br />
(STPCLK#)<br />
Internal CPU Clock<br />
External Clock<br />
(CLK)<br />
Hard Disk Drive On* Standby (spin down)<br />
Display On* Off<br />
* Power saving timeouts can be configured independently for these devices allowing them to enter a low-power<br />
state while the system is in Idle mode.<br />
Note that this table does not depict a precise timing diagram. <strong>The</strong> illustrations given in this table are intended to<br />
show the relative characteristic activity of these signals.<br />
Standby Mode 7<br />
Standby mode is entered when the Standby Mode Timeout (configured in the BIOS) occurs. <strong>The</strong> CPU,<br />
supporting chip set, and RAM remain powered, however, the CPU’s internal clock is stopped (stopping<br />
the CPU) as indicated in Table 7-4. Any user activity that generates an interrupt will cause a transition out<br />
of the Standby state to the Fully On state. <strong>The</strong> hard disk drive is forced into standby mode (spun down)<br />
when the standby mode timeout occurs. Note however, that the hard disk drive can be configured to spin<br />
down earlier by setting the HDD Spin-down Timeout BIOS option. <strong>The</strong> display system (including<br />
backlight) is also turned off when the standby timeout occurs. <strong>The</strong> display can also be configured to turn<br />
off earlier by setting the Video Timeout BIOS option.<br />
Suspend Modes 7<br />
<strong>The</strong> system can be configured to use one of two different Suspend modes: Suspend-to-Disk or<br />
Suspend-to-RAM. (<strong>The</strong>se two modes are also referred to as “normal” and “save-to-disk” in some related<br />
documents.) System power activity in each of these modes is described below. (Refer to Chapter 2 for<br />
information on selecting the suspend mode in the BIOS.)<br />
Suspend-to-RAM State 7<br />
In the Suspend-to-RAM state, power is maintained to RAM, video memory, and resume circuitry while<br />
all other system circuitry and power managed devices are powered off. <strong>The</strong> PC Card slots will also<br />
remain powered if the Resume On Modem Ring option is enable in the BIOS. Pressing the Suspend/<br />
Resume button, or a resume request generated by a modem ring will cause a transition to the Fully On<br />
state. <strong>The</strong> Suspend-to-RAM state is best suited for applications where system operation is suspended<br />
frequently and a quick resume time is desired.<br />
7-6 System Power