Vol 43 # 2 June 2011 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 43 # 2 June 2011 - Kma.org.kw
Vol 43 # 2 June 2011 - Kma.org.kw
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
140<br />
Macroinvasive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Presenting as Internal Jugular Vein Tumor Thrombus<br />
<strong>June</strong> <strong>2011</strong><br />
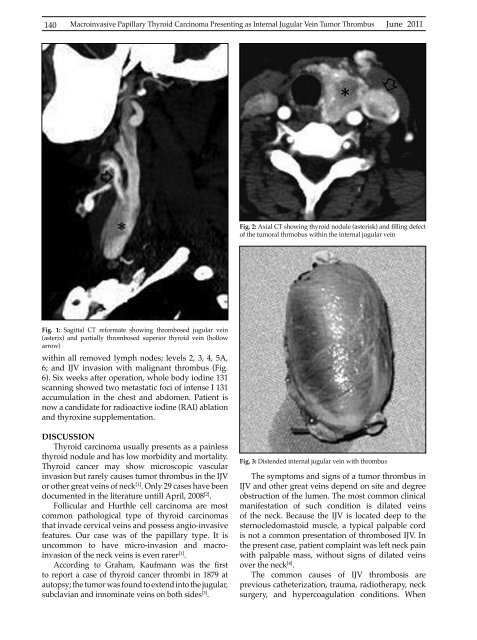
Fig. 2: Axial CT showing thyroid nodule (asterisk) and filling defect<br />
of the tumoral thrmobus within the internal jugular vein<br />
Fig. 1: Sagittal CT reformate showing thrombosed jugular vein<br />
(asterix) and partially thrombosed superior thyroid vein (hollow<br />
arrow)<br />
within all removed lymph nodes; levels 2, 3, 4, 5A,<br />
6; and IJV invasion with malignant thrombus (Fig.<br />
6). Six weeks after operation, whole body iodine 131<br />
scanning showed two metastatic foci of intense I 131<br />
accumulation in the chest and abdomen. Patient is<br />
now a candidate for radioactive iodine (RAI) ablation<br />
and thyroxine supplementation.<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Thyroid carcinoma usually presents as a painless<br />
thyroid nodule and has low morbidity and mortality.<br />
Thyroid cancer may show microscopic vascular<br />
invasion but rarely causes tumor thrombus in the IJV<br />
or other great veins of neck [1] . Only 29 cases have been<br />
documented in the literature untill April, 2008 [2] .<br />
Follicular and Hurthle cell carcinoma are most<br />
common pathological type of thyroid carcinomas<br />
that invade cervical veins and possess angio-invasive<br />
features. Our case was of the papillary type. It is<br />
uncommon to have micro-invasion and macroinvasion<br />
of the neck veins is even rarer [1] .<br />
According to Graham, Kaufmann was the first<br />
to report a case of thyroid cancer thrombi in 1879 at<br />
autopsy; the tumor was found to extend into the jugular,<br />
subclavian and innominate veins on both sides [3] .<br />
Fig. 3: Distended internal jugular vein with thrombus<br />
The symptoms and signs of a tumor thrombus in<br />
IJV and other great veins depend on site and degree<br />
obstruction of the lumen. The most common clinical<br />
manifestation of such condition is dilated veins<br />
of the neck. Because the IJV is located deep to the<br />
sternocledomastoid muscle, a typical palpable cord<br />
is not a common presentation of thrombosed IJV. In<br />
the present case, patient complaint was left neck pain<br />
with palpable mass, without signs of dilated veins<br />
over the neck [4] .<br />
The common causes of IJV thrombosis are<br />
previous catheterization, trauma, radiotherapy, neck<br />
surgery, and hypercoagulation conditions. When