201303.pdf 36567KB Mar 22 2013 09:11:22 PM
201303.pdf 36567KB Mar 22 2013 09:11:22 PM
201303.pdf 36567KB Mar 22 2013 09:11:22 PM
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
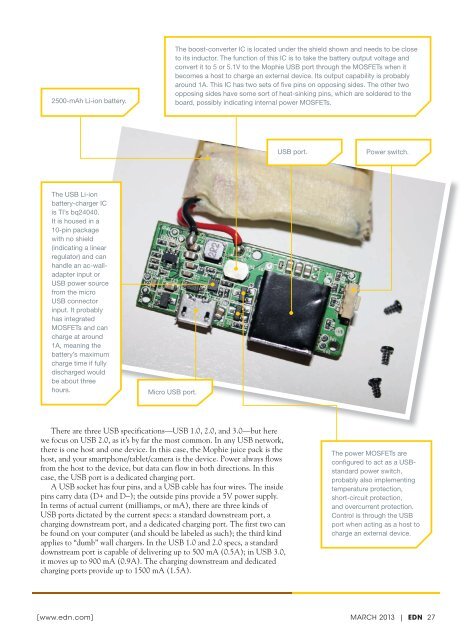
2500-mAh Li-ion battery.<br />
The boost-converter IC is located under the shield shown and needs to be close<br />
to its inductor. The function of this IC is to take the battery output voltage and<br />
convert it to 5 or 5.1V to the Mophie USB port through the MOSFETs when it<br />
becomes a host to charge an external device. Its output capability is probably<br />
around 1A. This IC has two sets of five pins on opposing sides. The other two<br />
opposing sides have some sort of heat-sinking pins, which are soldered to the<br />
board, possibly indicating internal power MOSFETs.<br />
USB port.<br />
Power switch.<br />
The USB Li-ion<br />
battery-charger IC<br />
is TI’s bq24040.<br />
It is housed in a<br />
10-pin package<br />
with no shield<br />
(indicating a linear<br />
regulator) and can<br />
handle an ac-walladapter<br />
input or<br />
USB power source<br />
from the micro<br />
USB connector<br />
input. It probably<br />
has integrated<br />
MOSFETs and can<br />
charge at around<br />
1A, meaning the<br />
battery’s maximum<br />
charge time if fully<br />
discharged would<br />
be about three<br />
hours.<br />
Micro USB port.<br />
There are three USB specifications—USB 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0—but here<br />
we focus on USB 2.0, as it’s by far the most common. In any USB network,<br />
there is one host and one device. In this case, the Mophie juice pack is the<br />
host, and your smartphone/tablet/camera is the device. Power always flows<br />
from the host to the device, but data can flow in both directions. In this<br />
case, the USB port is a dedicated charging port.<br />
A USB socket has four pins, and a USB cable has four wires. The inside<br />
pins carry data (D+ and D−); the outside pins provide a 5V power supply.<br />
In terms of actual current (milliamps, or mA), there are three kinds of<br />
USB ports dictated by the current specs: a standard downstream port, a<br />
charging downstream port, and a dedicated charging port. The first two can<br />
be found on your computer (and should be labeled as such); the third kind<br />
applies to “dumb” wall chargers. In the USB 1.0 and 2.0 specs, a standard<br />
downstream port is capable of delivering up to 500 mA (0.5A); in USB 3.0,<br />
it moves up to 900 mA (0.9A). The charging downstream and dedicated<br />
charging ports provide up to 1500 mA (1.5A).<br />
The power MOSFETs are<br />
configured to act as a USBstandard<br />
power switch,<br />
probably also implementing<br />
temperature protection,<br />
short-circuit protection,<br />
and overcurrent protection.<br />
Control is through the USB<br />
port when acting as a host to<br />
charge an external device.<br />
[ www.edn.com ] MARCH <strong>2013</strong> | EDN 27





![[270].pdf 37407KB Sep 02 2010 09:55:57 AM - ElectronicsAndBooks](https://img.yumpu.com/50350834/1/185x260/270pdf-37407kb-sep-02-2010-095557-am-electronicsandbooks.jpg?quality=85)
![draaien, A Viruly 1935 OCR c20130324 [320]. - ElectronicsAndBooks](https://img.yumpu.com/49957773/1/190x252/draaien-a-viruly-1935-ocr-c20130324-320-electronicsandbooks.jpg?quality=85)



![20051110 c20051031 [105].pdf 35001KB Feb 18 2009 08:46:32 PM](https://img.yumpu.com/48687202/1/190x253/20051110-c20051031-105pdf-35001kb-feb-18-2009-084632-pm.jpg?quality=85)





