Extraction Technologies For Medicinal And Aromatic Plants - Unido
Extraction Technologies For Medicinal And Aromatic Plants - Unido
Extraction Technologies For Medicinal And Aromatic Plants - Unido
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
EXTRACTION TECHNOLOGIES FOR MEDICINAL AND AROMATIC PLANTS<br />
odor similar to that of the oil. Thus, this condensate has some value. The<br />
sale of rose water (otto of rose) for use in weddings in the sub-continent is<br />
probably the only way by which the distiller realizes the value of the condensate.<br />
In practically all other cases, the condensate is wasted. Table 2 gives<br />
estimates of the values of wasted oil in the condensate in India for some<br />
essential oils. The estimate is conservative because it does not include oil<br />
physically carried with the condensate. Even this conservative estimate is a<br />
mind-boggling number and is particularly important in the social context of<br />
developing countries like India where marginal farmers are main contributors<br />
to the overall produce. The value of the recovered oil from central distillation<br />
facilities and pro rata distribution of the value will be a big bonus to the<br />
small farmer and can certainly stop the downslide. Table 2 shows a major<br />
contribution from Mentha arvensis. If the relatively high value fl avor sector is<br />
included, for India alone the value of wasted oil can easily reach US$ 100<br />
million. On a rough estimate, the combined number for the South East Asian<br />
countries can be upwards of US$ 160 million. It must be noted that these<br />
numbers are simple statistics. They do not refl ect in any way the high value<br />
that can be gained when the recovered oil is blended with the main distilled<br />
oil fraction to obtain a premium grade of the respective essential oil.<br />
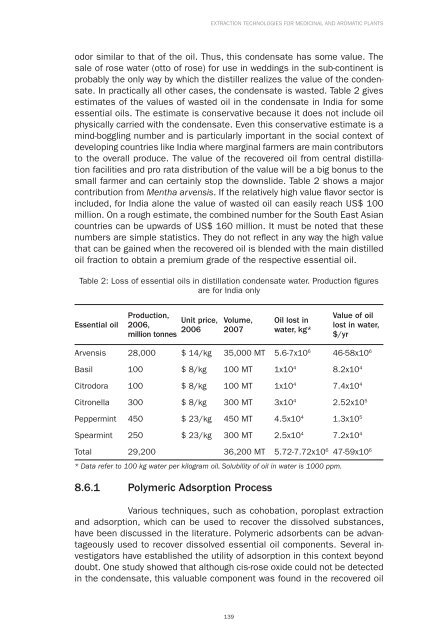
Table 2: Loss of essential oils in distillation condensate water. Production fi gures<br />
are for India only<br />
Essential oil<br />
Production,<br />
2006,<br />
million tonnes<br />
Unit price,<br />
2006<br />
Volume,<br />
2007<br />
139<br />
Oil lost in<br />
water, kg*<br />
Value of oil<br />
lost in water,<br />
$/yr<br />
Arvensis 28,000 $ 14/kg 35,000 MT 5.6-7x10 6 46-58x10 6<br />
Basil 100 $ 8/kg 100 MT 1x10 4 8.2x10 4<br />
Citrodora 100 $ 8/kg 100 MT 1x10 4 7.4x10 4<br />
Citronella 300 $ 8/kg 300 MT 3x10 4 2.52x10 5<br />
Peppermint 450 $ 23/kg 450 MT 4.5x10 4 1.3x10 5<br />
Spearmint 250 $ 23/kg 300 MT 2.5x10 4 7.2x10 4<br />
Total 29,200 36,200 MT 5.72-7.72x10 6 47-59x10 6<br />
* Data refer to 100 kg water per kilogram oil. Solubility of oil in water is 1000 ppm.<br />
8.6.1 Polymeric Adsorption Process<br />
Various techniques, such as cohobation, poroplast extraction<br />
and adsorption, which can be used to recover the dissolved substances,<br />
have been discussed in the literature. Polymeric adsorbents can be advantageously<br />
used to recover dissolved essential oil components. Several investigators<br />
have established the utility of adsorption in this context beyond<br />
doubt. One study showed that although cis-rose oxide could not be detected<br />
in the condensate, this valuable component was found in the recovered oil