SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
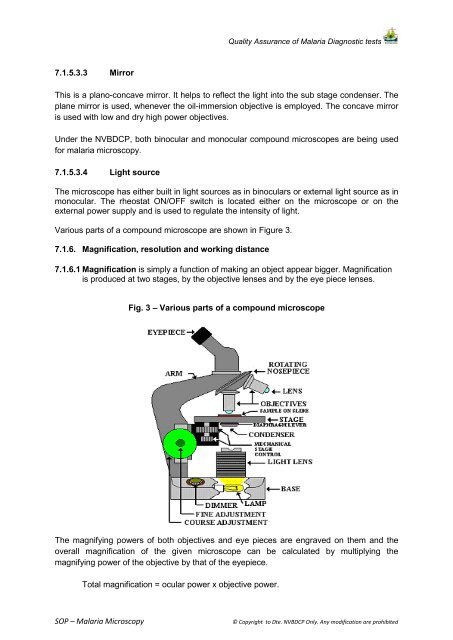
Quality Assurance of <strong>Malaria</strong> Diagnostic tests7.1.5.3.3 MirrorThis is a plano-concave mirror. It helps to reflect the light into the sub stage condenser. Theplane mirror is used, whenever the oil-immersion objective is employed. The concave mirroris used with low and dry high power objectives.Under the <strong>NVBDCP</strong>, both binocular and monocular compound microscopes are being usedfor malaria microscopy.7.1.5.3.4 Light sourceThe microscope has either built in light sources as in binoculars or external light source as inmonocular. The rheostat ON/OFF switch is located either on the microscope or on theexternal power supply and is used to regulate the intensity of light.Various parts of a compound microscope are shown in Figure 3.7.1.6. Magnification, resolution and working distance7.1.6.1 Magnification is simply a function of making an object appear bigger. Magnificationis produced at two stages, by the objective lenses and by the eye piece lenses.Fig. 3 – Various parts of a compound microscopeThe magnifying powers of both objectives and eye pieces are engraved on them and theoverall magnification of the given microscope can be calculated by multiplying themagnifying power of the objective by that of the eyepiece.Total magnification = ocular power x objective power.<strong>SOP</strong> – <strong>Malaria</strong> <strong>Microscopy</strong>© Copyright to Dte. <strong>NVBDCP</strong> Only. Any modification are prohibited