SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
SOP â Malaria Microscopy - NVBDCP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
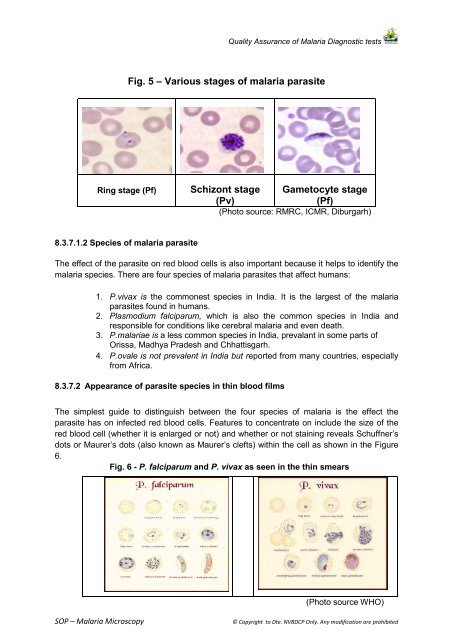
Quality Assurance of <strong>Malaria</strong> Diagnostic testsFig. 5 – Various stages of malaria parasiteRing stage (Pf)Schizont stage Gametocyte stage(Pv)(Pf)(Photo source: RMRC, ICMR, Diburgarh)8.3.7.1.2 Species of malaria parasiteThe effect of the parasite on red blood cells is also important because it helps to identify themalaria species. There are four species of malaria parasites that affect humans:1. P.vivax is the commonest species in India. It is the largest of the malariaparasites found in humans.2. Plasmodium falciparum, which is also the common species in India andresponsible for conditions like cerebral malaria and even death.3. P.malariae is a less common species in India, prevalant in some parts ofOrissa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.4. P.ovale is not prevalent in India but reported from many countries, especiallyfrom Africa.8.3.7.2 Appearance of parasite species in thin blood filmsThe simplest guide to distinguish between the four species of malaria is the effect theparasite has on infected red blood cells. Features to concentrate on include the size of thered blood cell (whether it is enlarged or not) and whether or not staining reveals Schuffner’sdots or Maurer’s dots (also known as Maurer’s clefts) within the cell as shown in the Figure6.Fig. 6 - P. falciparum and P. vivax as seen in the thin smears(Photo source WHO)<strong>SOP</strong> – <strong>Malaria</strong> <strong>Microscopy</strong>© Copyright to Dte. <strong>NVBDCP</strong> Only. Any modification are prohibited