D E S C R I P T I O N O F W O R K - MEGAPOLI - Dmi
D E S C R I P T I O N O F W O R K - MEGAPOLI - Dmi
D E S C R I P T I O N O F W O R K - MEGAPOLI - Dmi
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>MEGAPOLI</strong> 212520<br />
Paris and London are the only two cities within the European Union that strictly correspond to the<br />
definition of a megacity (i.e. population larger than 5 million people). The Rhine-Ruhr and Po<br />
Valley areas have megacity features even if they can be better described as urban conglomerations<br />
than as a single metropolitan area (Figure 5). The estimated loss of life expectancy due to air<br />
pollution is quite high in these areas (Figure 6) and therefore, attaining the air pollutant<br />
concentration limits, imposed by the EC air quality framework, and daughter directives is presently<br />
critical for different air pollutants, e.g. PM and NO2.<br />
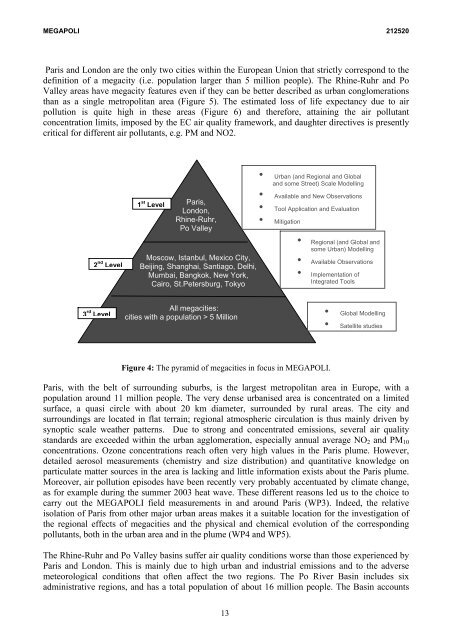
2 nd Level<br />
3 rd Level<br />
1 st Level<br />
Paris,<br />
London,<br />
Rhine-Ruhr,<br />
Po Valley<br />
Moscow, Istanbul, Mexico City,<br />
Beijing, Shanghai, Santiago, Delhi,<br />
Mumbai, Bangkok, New York,<br />
Cairo, St.Petersburg, Tokyo<br />
All megacities:<br />
cities with a population > 5 Million<br />
Figure 4: The pyramid of megacities in focus in <strong>MEGAPOLI</strong>.<br />
Paris, with the belt of surrounding suburbs, is the largest metropolitan area in Europe, with a<br />
population around 11 million people. The very dense urbanised area is concentrated on a limited<br />
surface, a quasi circle with about 20 km diameter, surrounded by rural areas. The city and<br />
surroundings are located in flat terrain; regional atmospheric circulation is thus mainly driven by<br />
synoptic scale weather patterns. Due to strong and concentrated emissions, several air quality<br />
standards are exceeded within the urban agglomeration, especially annual average NO2 and PM10<br />
concentrations. Ozone concentrations reach often very high values in the Paris plume. However,<br />
detailed aerosol measurements (chemistry and size distribution) and quantitative knowledge on<br />
particulate matter sources in the area is lacking and little information exists about the Paris plume.<br />
Moreover, air pollution episodes have been recently very probably accentuated by climate change,<br />
as for example during the summer 2003 heat wave. These different reasons led us to the choice to<br />
carry out the <strong>MEGAPOLI</strong> field measurements in and around Paris (WP3). Indeed, the relative<br />
isolation of Paris from other major urban areas makes it a suitable location for the investigation of<br />
the regional effects of megacities and the physical and chemical evolution of the corresponding<br />
pollutants, both in the urban area and in the plume (WP4 and WP5).<br />
The Rhine-Ruhr and Po Valley basins suffer air quality conditions worse than those experienced by<br />
Paris and London. This is mainly due to high urban and industrial emissions and to the adverse<br />
meteorological conditions that often affect the two regions. The Po River Basin includes six<br />
administrative regions, and has a total population of about 16 million people. The Basin accounts<br />
13<br />
• Urban (and Regional and Global<br />
and some Street) Scale Modelling<br />
• Available and New Observations<br />
• Tool Application and Evaluation<br />
• Mitigation<br />
• Regional (and Global and<br />
some Urban) Modelling<br />
• Available Observations<br />
• Implementation of<br />
Integrated Tools<br />
• Global Modelling<br />
• Satellite studies