Applied Superconductivity - Walther Meißner Institut - Bayerische ...
Applied Superconductivity - Walther Meißner Institut - Bayerische ...
Applied Superconductivity - Walther Meißner Institut - Bayerische ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
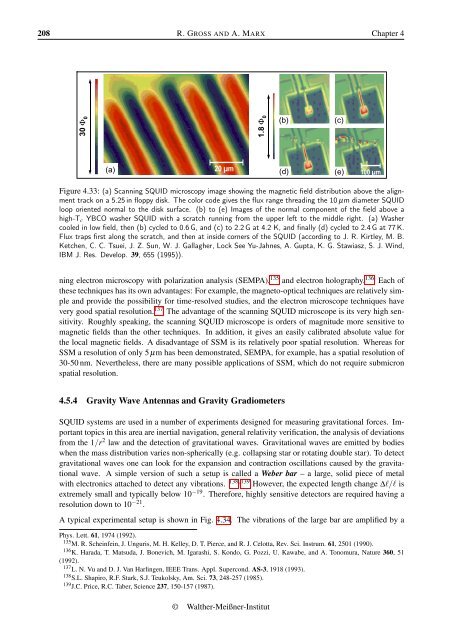
208 R. GROSS AND A. MARX Chapter 430 Φ 01.8 Φ 0(b)(c)(a)20 µm(d)(e)100 µmFigure 4.33: (a) Scanning SQUID microscopy image showing the magnetic field distribution above the alignmenttrack on a 5.25 in floppy disk. The color code gives the flux range threading the 10 µm diameter SQUIDloop oriented normal to the disk surface. (b) to (e) Images of the normal component of the field above ahigh-T c YBCO washer SQUID with a scratch running from the upper left to the middle right. (a) Washercooled in low field, then (b) cycled to 0.6 G, and (c) to 2.2 G at 4.2 K, and finally (d) cycled to 2.4 G at 77 K.Flux traps first along the scratch, and then at inside corners of the SQUID (according to J. R. Kirtley, M. B.Ketchen, C. C. Tsuei, J. Z. Sun, W. J. Gallagher, Lock See Yu-Jahnes, A. Gupta, K. G. Stawiasz, S. J. Wind,IBM J. Res. Develop. 39, 655 (1995)).ning electron microscopy with polarization analysis (SEMPA), 135 and electron holography. 136 Each ofthese techniques has its own advantages: For example, the magneto-optical techniques are relatively simpleand provide the possibility for time-resolved studies, and the electron microscope techniques havevery good spatial resolution. 137 The advantage of the scanning SQUID microscope is its very high sensitivity.Roughly speaking, the scanning SQUID microscope is orders of magnitude more sensitive tomagnetic fields than the other techniques. In addition, it gives an easily calibrated absolute value forthe local magnetic fields. A disadvantage of SSM is its relatively poor spatial resolution. Whereas forSSM a resolution of only 5 µm has been demonstrated, SEMPA, for example, has a spatial resolution of30-50 nm. Nevertheless, there are many possible applications of SSM, which do not require submicronspatial resolution.4.5.4 Gravity Wave Antennas and Gravity GradiometersSQUID systems are used in a number of experiments designed for measuring gravitational forces. Importanttopics in this area are inertial navigation, general relativity verification, the analysis of deviationsfrom the 1/r 2 law and the detection of gravitational waves. Gravitational waves are emitted by bodieswhen the mass distribution varies non-spherically (e.g. collapsing star or rotating double star). To detectgravitational waves one can look for the expansion and contraction oscillations caused by the gravitationalwave. A simple version of such a setup is called a Weber bar – a large, solid piece of metalwith electronics attached to detect any vibrations. 138,139 However, the expected length change ∆l/l isextremely small and typically below 10 −19 . Therefore, highly sensitive detectors are required having aresolution down to 10 −21 .A typical experimental setup is shown in Fig. 4.34. The vibrations of the large bar are amplified by aPhys. Lett. 61, 1974 (1992).135 M. R. Scheinfein, J. Unguris, M. H. Kelley, D. T. Pierce, and R. J. Celotta, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61, 2501 (1990).136 K. Harada, T. Matsuda, J. Bonevich, M. Igarashi, S. Kondo, G. Pozzi, U. Kawabe, and A. Tonomura, Nature 360, 51(1992).137 L. N. Vu and D. J. Van Harlingen, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. AS-3, 1918 (1993).138 S.L. Shapiro, R.F. Stark, S.J. Teukolsky, Am. Sci. 73, 248-257 (1985).139 J.C. Price, R.C. Taber, Science 237, 150-157 (1987).© <strong>Walther</strong>-Meißner-<strong>Institut</strong>