Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence Contents
Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence Contents
Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence Contents
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
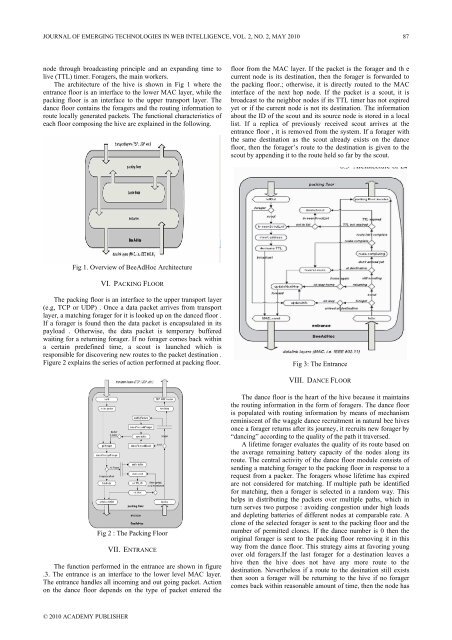
JOURNAL OF EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES IN WEB INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 2, NO. 2, MAY 2010 87node through broadcast<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciple and an expand<strong>in</strong>g time tolive (TTL) timer. Foragers, the ma<strong>in</strong> workers.The architecture <strong>of</strong> the hive is shown <strong>in</strong> Fig 1 where theentrance floor is an <strong>in</strong>terface to the lower MAC layer, while thepack<strong>in</strong>g floor is an <strong>in</strong>terface to the upper transport layer. Thedance floor conta<strong>in</strong>s the foragers and the rout<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation toroute locally generated packets. The functional characteristics <strong>of</strong>each floor compos<strong>in</strong>g the hive are expla<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> the follow<strong>in</strong>g.floor from the MAC layer. If the packet is the forager and th ecurrent node is its dest<strong>in</strong>ation, then the forager is forwarded tothe pack<strong>in</strong>g floor.; otherwise, it is directly routed to the MAC<strong>in</strong>terface <strong>of</strong> the next hop node. If the packet is a scout, it isbroadcast to the neighbor nodes if its TTL timer has not expiredyet or if the current node is not its dest<strong>in</strong>ation. The <strong>in</strong>formationabout the ID <strong>of</strong> the scout and its source node is stored <strong>in</strong> a locallist. If a replica <strong>of</strong> previously received scout arrives at theentrance floor , it is removed from the system. If a forager withthe same dest<strong>in</strong>ation as the scout already exists on the dancefloor, then the forager’s route to the dest<strong>in</strong>ation is given to thescout by append<strong>in</strong>g it to the route held so far by the scout.Fig 1. Overview <strong>of</strong> BeeAdHoc ArchitectureVI. PACKING FLOORThe pack<strong>in</strong>g floor is an <strong>in</strong>terface to the upper transport layer(e.g, TCP or UDP) . Once a data packet arrives from transportlayer, a match<strong>in</strong>g forager for it is looked up on the danced floor .If a forager is found then the data packet is encapsulated <strong>in</strong> itspayload . Otherwise, the data packet is temporary bufferedwait<strong>in</strong>g for a return<strong>in</strong>g forager. If no forager comes back with<strong>in</strong>a certa<strong>in</strong> predef<strong>in</strong>ed time, a scout is launched which isresponsible for discover<strong>in</strong>g new routes to the packet dest<strong>in</strong>ation .Figure 2 expla<strong>in</strong>s the series <strong>of</strong> action performed at pack<strong>in</strong>g floor.Fig 3: The EntranceVIII. DANCE FLOORFig 2 : The Pack<strong>in</strong>g FloorVII. ENTRANCEThe function performed <strong>in</strong> the entrance are shown <strong>in</strong> figure.3. The entrance is an <strong>in</strong>terface to the lower level MAC layer.The entrance handles all <strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g and out go<strong>in</strong>g packet. Actionon the dance floor depends on the type <strong>of</strong> packet entered theThe dance floor is the heart <strong>of</strong> the hive because it ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>sthe rout<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation <strong>in</strong> the form <strong>of</strong> foragers. The dance flooris populated with rout<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation by means <strong>of</strong> mechanismrem<strong>in</strong>iscent <strong>of</strong> the waggle dance recruitment <strong>in</strong> natural bee hivesonce a forager returns after its journey, it recruits new forager by“danc<strong>in</strong>g” accord<strong>in</strong>g to the quality <strong>of</strong> the path it traversed.A lifetime forager evaluates the quality <strong>of</strong> its route based onthe average rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g battery capacity <strong>of</strong> the nodes along itsroute. The central activity <strong>of</strong> the dance floor module consists <strong>of</strong>send<strong>in</strong>g a match<strong>in</strong>g forager to the pack<strong>in</strong>g floor <strong>in</strong> response to arequest from a packer. The foragers whose lifetime has expiredare not considered for match<strong>in</strong>g. If multiple path be identifiedfor match<strong>in</strong>g, then a forager is selected <strong>in</strong> a random way. Thishelps <strong>in</strong> distribut<strong>in</strong>g the packets over multiple paths, which <strong>in</strong>turn serves two purpose : avoid<strong>in</strong>g congestion under high loadsand deplet<strong>in</strong>g batteries <strong>of</strong> different nodes at comparable rate. Aclone <strong>of</strong> the selected forager is sent to the pack<strong>in</strong>g floor and thenumber <strong>of</strong> permitted clones. If the dance number is 0 then theorig<strong>in</strong>al forager is sent to the pack<strong>in</strong>g floor remov<strong>in</strong>g it <strong>in</strong> thisway from the dance floor. This strategy aims at favor<strong>in</strong>g youngover old foragers.If the last forager for a dest<strong>in</strong>ation leaves ahive then the hive does not have any more route to thedest<strong>in</strong>ation. Nevertheless if a route to the des<strong>in</strong>ation still existsthen soon a forager will be return<strong>in</strong>g to the hive if no foragercomes back with<strong>in</strong> reasonable amount <strong>of</strong> time, then the node has© 2010 ACADEMY PUBLISHER