Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
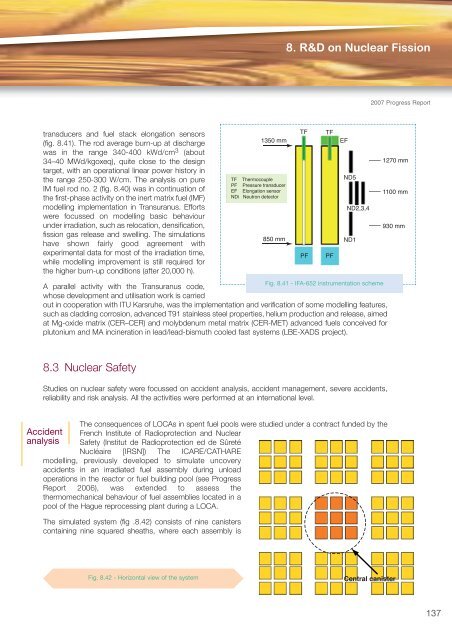
8. R&D on Nuclear Fission2007 Progress Reporttransducers and fuel stack elongation sensorsTF TF(fig. 8.41). The rod average burn-up at discharge1350 mmEFwas in the range 340-400 kWd/cm 3 (about34–40 MWd/kgoxeq), quite close to the design1270 mmtarget, with an operational linear power history inthe range 250-300 W/cm. The analysis on pureTF ThermocoupleND5PF Pressure transducerIM fuel rod no. 2 (fig. 8.40) was in continuation ofEF Elongation sensorthe first-phase activity on the inert matrix fuel (IMF)NDi Neutron detector1100 mmmodelling implementation in Transuranus. EffortsND2,3,4were focussed on modelling basic behaviourunder irradiation, such as relocation, densification,930 mmfission gas release and swelling. The simulationshave shown fairly good agreement with850 mmND1experimental data for most of the irradiation time,while modelling improvement is still required forthe higher burn-up conditions (after 20,000 h).PF PFA parallel activity with the Transuranus code,Fig. 8.41 - IFA-652 instrumentation schemewhose development and utilisation work is carriedout in cooperation with ITU Karsruhe, was the implementation and verification of some modelling features,such as cladding corrosion, advanced T91 stainless steel properties, helium production and release, aimedat Mg-oxide matrix (CER–CER) and molybdenum metal matrix (CER-MET) advanced fuels conceived forplutonium and MA incineration in lead/lead-bismuth cooled fast systems (LBE-XADS project).8.3 Nuclear SafetyStudies on nuclear safety were focussed on accident analysis, accident management, severe accidents,reliability and risk analysis. All the activities were performed at an international level.The consequences of LOCAs in spent fuel pools were studied under a contract funded by theAccident French Institute of Radioprotection and Nuclearanalysis Safety (Institut de Radioprotection ed de SûretéNucléaire [IRSN]) The ICARE/CATHAREmodelling, previously developed to simulate uncoveryaccidents in an irradiated fuel assembly during unloadoperations in the reactor or fuel building pool (see ProgressReport 2006), was extended to assess thethermomechanical behaviour of fuel assemblies located in apool of the Hague reprocessing plant during a LOCA.The simulated system (fig .8.42) consists of nine canisterscontaining nine squared sheaths, where each assembly isFig. 8.42 - Horizontal view of the systemCentral canister137