Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
Fusion Programme - ENEA - Fusione
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
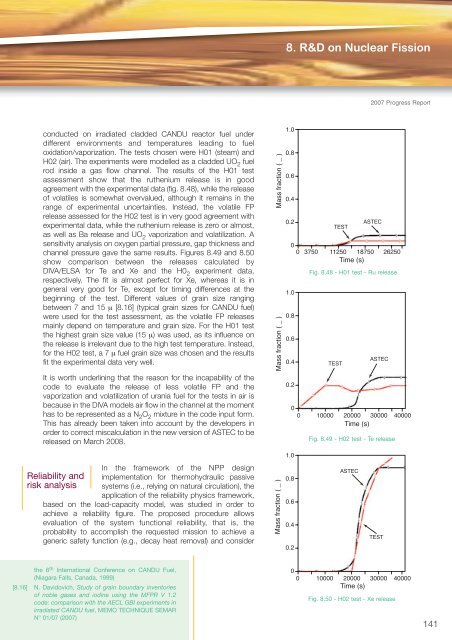
8. R&D on Nuclear Fission2007 Progress Reportconducted on irradiated cladded CANDU reactor fuel underdifferent environments and temperatures leading to fueloxidation/vaporization. The tests chosen were H01 (steam) andH02 (air). The experiments were modelled as a cladded UO 2 fuelrod inside a gas flow channel. The results of the H01 testassessment show that the ruthenium release is in goodagreement with the experimental data (fig. 8.48), while the releaseof volatiles is somewhat overvalued, although it remains in therange of experimental uncertainties. Instead, the volatile FPrelease assessed for the H02 test is in very good agreement withexperimental data, while the ruthenium release is zero or almost,as well as Ba release and UO 2 vaporization and volatilization. Asensitivity analysis on oxygen partial pressure, gap thickness andchannel pressure gave the same results. Figures 8.49 and 8.50show comparison between the releases calculated byDIVA/ELSA for Te and Xe and the H0 2 experiment data,respectively. The fit is almost perfect for Xe, whereas it is ingeneral very good for Te, except for timing differences at thebeginning of the test. Different values of grain size rangingbetween 7 and 15 μ [8.16] (typical grain sizes for CANDU fuel)were used for the test assessment, as the volatile FP releasesmainly depend on temperature and grain size. For the H01 testthe highest grain size value (15 μ) was used, as its influence onthe release is irrelevant due to the high test temperature. Instead,for the H02 test, a 7 μ fuel grain size was chosen and the resultsfit the experimental data very well.It is worth underlining that the reason for the incapability of thecode to evaluate the release of less volatile FP and thevaporization and volatilization of urania fuel for the tests in air isbecause in the DIVA models air flow in the channel at the momenthas to be represented as a N 2 O 2 mixture in the code input form.This has already been taken into account by the developers inorder to correct miscalculation in the new version of ASTEC to bereleased on March 2008.Mass fraction ( _ )Mass fraction ( _ )1.00.80.60.40.201.00.80.60.40.20TESTASTEC0 3750 11250 18750 26250Time (s)Fig. 8.48 - H01 test - Ru releaseTESTASTEC0 10000 20000 30000 40000Time (s)Fig. 8.49 - H02 test - Te release1.0In the framework of the NPP designReliability and implementation for thermohydraulic passiverisk analysis systems (i.e., relying on natural circulation), theapplication of the reliability physics framework,based on the load-capacity model, was studied in order toachieve a reliability figure. The proposed procedure allowsevaluation of the system functional reliability, that is, theprobability to accomplish the requested mission to achieve ageneric safety function (e.g., decay heat removal) and considerMass fraction ( _ )0.80.60.40.2ASTECTESTthe 6 th International Conference on CANDU Fuel,(Niagara Falls, Canada, 1999)[8.16] N. Davidovich, Study of grain boundary inventoriesof noble gases and iodine using the MFPR V 1.2code: comparison with the AECL GBI experiments inirradiated CANDU fuel, MEMO TECHNIQUE SEMARN° 01/07 (2007)00 10000 20000 30000 40000Time (s)Fig. 8.50 - H02 test - Xe release141