Measurement of the Jet Energy Scale in the CMS experiment ... - IIHE
Measurement of the Jet Energy Scale in the CMS experiment ... - IIHE
Measurement of the Jet Energy Scale in the CMS experiment ... - IIHE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
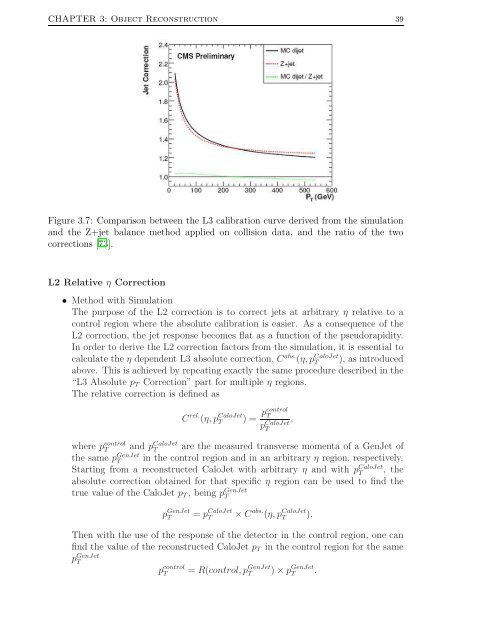
CHAPTER 3: Object Reconstruction 39Figure 3.7: Comparison between <strong>the</strong> L3 calibration curve derived from <strong>the</strong> simulationand <strong>the</strong> Z+jet balance method applied on collision data, and <strong>the</strong> ratio <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> twocorrections [73].L2 Relative η Correction• Method with SimulationThe purpose <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> L2 correction is to correct jets at arbitrary η relative to acontrol region where <strong>the</strong> absolute calibration is easier. As a consequence <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>L2 correction, <strong>the</strong> jet response becomes flat as a function <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> pseudorapidity.In order to derive <strong>the</strong> L2 correction factors from <strong>the</strong> simulation, it is essential tocalculate <strong>the</strong> η dependent L3 absolute correction, C abs. (η, p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T ), as <strong>in</strong>troducedabove. This is achieved by repeat<strong>in</strong>g exactly <strong>the</strong> same procedure described <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>“L3 Absolute p T Correction” part for multiple η regions.The relative correction is def<strong>in</strong>ed asC rel. (η, p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T) = pcontrol T,p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>Twhere p controlT and p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T are <strong>the</strong> measured transverse momenta <strong>of</strong> a Gen<strong>Jet</strong> <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> same p Gen<strong>Jet</strong>T <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> control region and <strong>in</strong> an arbitrary η region, respectively.Start<strong>in</strong>g from a reconstructed Calo<strong>Jet</strong> with arbitrary η and with p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T , <strong>the</strong>absolute correction obta<strong>in</strong>ed for that specific η region can be used to f<strong>in</strong>d <strong>the</strong>true value <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Calo<strong>Jet</strong> p T , be<strong>in</strong>g p Gen<strong>Jet</strong>Tp Gen<strong>Jet</strong>T= p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T× C abs. (η, p Calo<strong>Jet</strong>T ).Then with <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> response <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> detector <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> control region, one canf<strong>in</strong>d <strong>the</strong> value <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> reconstructed Calo<strong>Jet</strong> p T <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> control region for <strong>the</strong> samep Gen<strong>Jet</strong>Tp controlT= R(control, p Gen<strong>Jet</strong>T ) × p Gen<strong>Jet</strong>T .