Scheme of work Adventurous Activities key stage 2
Scheme of work Adventurous Activities key stage 2
Scheme of work Adventurous Activities key stage 2
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
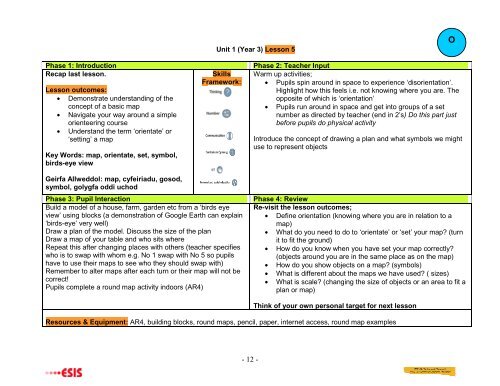
Unit 1 (Year 3) Lesson 5OPhase 1: IntroductionRecap last lesson.Lesson outcomes:• Demonstrate understanding <strong>of</strong> theconcept <strong>of</strong> a basic map• Navigate your way around a simpleorienteering course• Understand the term ‘orientate’ or‘setting’ a mapKey Words: map, orientate, set, symbol,birds-eye viewSkillsFrame<strong>work</strong>:Phase 2: Teacher InputWarm up activities;• Pupils spin around in space to experience ‘disorientation’.Highlight how this feels i.e. not knowing where you are. Theopposite <strong>of</strong> which is ‘orientation’• Pupils run around in space and get into groups <strong>of</strong> a setnumber as directed by teacher (end in 2’s) Do this part justbefore pupils do physical activityIntroduce the concept <strong>of</strong> drawing a plan and what symbols we mightuse to represent objectsGeirfa Allweddol: map, cyfeiriadu, gosod,symbol, golygfa oddi uchodPhase 3: Pupil InteractionBuild a model <strong>of</strong> a house, farm, garden etc from a ‘birds eyeview’ using blocks (a demonstration <strong>of</strong> Google Earth can explain‘birds-eye’ very well)Draw a plan <strong>of</strong> the model. Discuss the size <strong>of</strong> the planDraw a map <strong>of</strong> your table and who sits whereRepeat this after changing places with others (teacher specifieswho is to swap with whom e.g. No 1 swap with No 5 so pupilshave to use their maps to see who they should swap with)Remember to alter maps after each turn or their map will not becorrect!Pupils complete a round map activity indoors (AR4)Phase 4: ReviewRe-visit the lesson outcomes;• Define orientation (knowing where you are in relation to amap)• What do you need to do to ‘orientate’ or ‘set’ your map? (turnit to fit the ground)• How do you know when you have set your map correctly?(objects around you are in the same place as on the map)• How do you show objects on a map? (symbols)• What is different about the maps we have used? ( sizes)• What is scale? (changing the size <strong>of</strong> objects or an area to fit aplan or map)Think <strong>of</strong> your own personal target for next lessonResources & Equipment: AR4, building blocks, round maps, pencil, paper, internet access, round map examples- 12