Association
Magnetic Oxide Heterostructures: EuO on Cubic Oxides ... - JuSER
Magnetic Oxide Heterostructures: EuO on Cubic Oxides ... - JuSER
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.3. Magnetic properties of EuO 15<br />
order to maintain the insulating nature of EuO tunnel contacts. An exotic method to provide<br />
itinerant 5d electrons in EuO 1−x is by light doping using a laser irradiation of hv ≈ 2eV. 23<br />
Finally, if chemical constituents with different ionic radii are incorporated into the crystal,<br />
this gives rise to isotropic strain (chemical pressure). This chemical pressure is supposed to<br />
vary the f –f and d–f exchange interactions. 69<br />
2.3.2. Thin film effects in EuO<br />
<br />
d EuO = 5.1 nm<br />
<br />
n=20<br />
<br />
z<br />
S<br />
d EuO = 2.6 nm<br />
4<br />
n=7<br />
3<br />
n=5<br />
2<br />
n=4<br />
1<br />
n=3<br />
n=2<br />
0<br />
n=1<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70<br />
Temperature (K)<br />
n=10<br />
n=15<br />
surface Layer<br />
center Layer<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
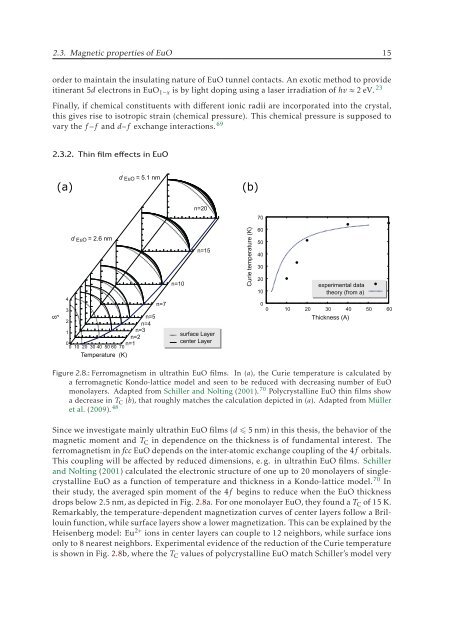
Figure 2.8.: Ferromagnetism in ultrathin EuO films. In (a), the Curie temperature is calculated by<br />
a ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice model and seen to be reduced with decreasing number of EuO<br />
monolayers. Adapted from Schiller and Nolting (2001). 70 Polycrystalline EuO thin films show<br />
a decrease in T C (b), that roughly matches the calculation depicted in (a). Adapted from Müller<br />
et al. (2009). 48<br />
Since we investigate mainly ultrathin EuO films (d 5 nm) in this thesis, the behavior of the<br />
magnetic moment and T C in dependence on the thickness is of fundamental interest. The<br />
ferromagnetism in fcc EuO depends on the inter-atomic exchange coupling of the 4f orbitals.<br />
This coupling will be affected by reduced dimensions, e. g. in ultrathin EuO films. Schiller<br />
and Nolting (2001) calculated the electronic structure of one up to 20 monolayers of singlecrystalline<br />
EuO as a function of temperature and thickness in a Kondo-lattice model. 70 In<br />
their study, the averaged spin moment of the 4f begins to reduce when the EuO thickness<br />
drops below 2.5 nm, as depicted in Fig. 2.8a. For one monolayer EuO, they found a T C of 15 K.<br />
Remarkably, the temperature-dependent magnetization curves of center layers follow a Brillouin<br />
function, while surface layers show a lower magnetization. This can be explained by the<br />
Heisenberg model: Eu 2+ ions in center layers can couple to 12 neighbors, while surface ions<br />
only to 8 nearest neighbors. Experimental evidence of the reduction of the Curie temperature<br />
is shown in Fig. 2.8b, where the T C values of polycrystalline EuO match Schiller’s model very