UNIVERSIT . . AT BONN Physikalisches Institut - Prof. Dr. Norbert ...
UNIVERSIT . . AT BONN Physikalisches Institut - Prof. Dr. Norbert ...
UNIVERSIT . . AT BONN Physikalisches Institut - Prof. Dr. Norbert ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.3. X-ray detector concepts 9<br />
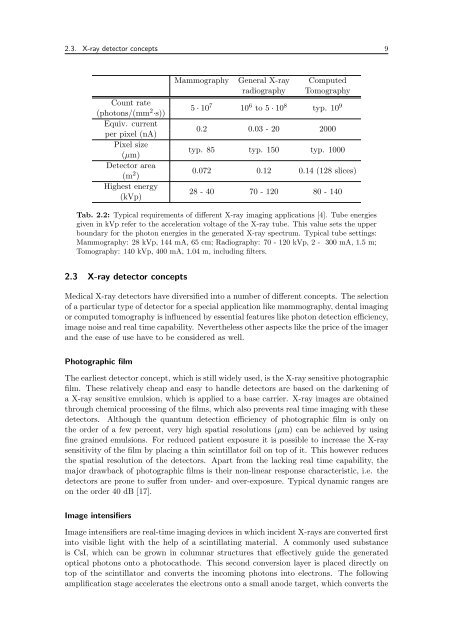
Count rate<br />
(photons/(mm2 ·s))<br />
Equiv. current<br />
per pixel (nA)<br />
Pixel size<br />
(µm)<br />
Detector area<br />
(m2 )<br />
Highest energy<br />
(kVp)<br />
Mammography General X-ray Computed<br />
radiography Tomography<br />
5 · 10 7 10 6 to 5 · 10 8 typ. 10 9<br />
0.2 0.03 - 20 2000<br />
typ. 85 typ. 150 typ. 1000<br />
0.072 0.12 0.14 (128 slices)<br />
28 - 40 70 - 120 80 - 140<br />
Tab. 2.2: Typical requirements of different X-ray imaging applications [4]. Tube energies<br />
given in kVp refer to the acceleration voltage of the X-ray tube. This value sets the upper<br />
boundary for the photon energies in the generated X-ray spectrum. Typical tube settings:<br />
Mammography: 28 kVp, 144 mA, 65 cm; Radiography: 70 - 120 kVp, 2 - 300 mA, 1.5 m;<br />
Tomography: 140 kVp, 400 mA, 1.04 m, including filters.<br />
2.3 X-ray detector concepts<br />
Medical X-ray detectors have diversified into a number of different concepts. The selection<br />
of a particular type of detector for a special application like mammography, dental imaging<br />
or computed tomography is influenced by essential features like photon detection efficiency,<br />
image noise and real time capability. Nevertheless other aspects like the price of the imager<br />
and the ease of use have to be considered as well.<br />
Photographic film<br />
The earliest detector concept, which is still widely used, is the X-ray sensitive photographic<br />
film. These relatively cheap and easy to handle detectors are based on the darkening of<br />
a X-ray sensitive emulsion, which is applied to a base carrier. X-ray images are obtained<br />
through chemical processing of the films, which also prevents real time imaging with these<br />
detectors. Although the quantum detection efficiency of photographic film is only on<br />
the order of a few percent, very high spatial resolutions (µm) can be achieved by using<br />
fine grained emulsions. For reduced patient exposure it is possible to increase the X-ray<br />
sensitivity of the film by placing a thin scintillator foil on top of it. This however reduces<br />
the spatial resolution of the detectors. Apart from the lacking real time capability, the<br />
major drawback of photographic films is their non-linear response characteristic, i.e. the<br />
detectors are prone to suffer from under- and over-exposure. Typical dynamic ranges are<br />
on the order 40 dB [17].<br />
Image intensifiers<br />
Image intensifiers are real-time imaging devices in which incident X-rays are converted first<br />
into visible light with the help of a scintillating material. A commonly used substance<br />
is CsI, which can be grown in columnar structures that effectively guide the generated<br />
optical photons onto a photocathode. This second conversion layer is placed directly on<br />
top of the scintillator and converts the incoming photons into electrons. The following<br />
amplification stage accelerates the electrons onto a small anode target, which converts the