LANAGRO-MG: EXCELÃNCIA E VALORIZAÃÃO DA ... - CRMV-MG
LANAGRO-MG: EXCELÃNCIA E VALORIZAÃÃO DA ... - CRMV-MG
LANAGRO-MG: EXCELÃNCIA E VALORIZAÃÃO DA ... - CRMV-MG
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
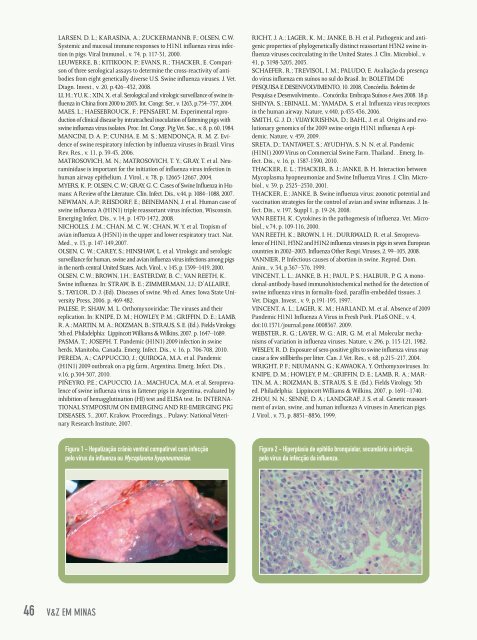
LARSEN, D. L.; KARASINA, A.; ZUCKERMANNB, F.; OLSEN, C.W.Systemic and mucosal immune responses to H1N1 influenza virus infectionin pigs. Viral Immunol., v. 74, p. 117-31, 2000.LEUWERKE, B.; KITIKOON, P.; EVANS, R.; THACKER, E. Comparisonof three serological assays to determine the cross-reactivity of antibodiesfrom eight genetically diverse U.S. Swine influenza viruses. J. Vet.Diagn. Invest., v. 20, p.426–432, 2008.LI, H.; YU, K.; XIN, X. et al. Serological and virologic surveillance of swine influenzain China from 2000 to 2003. Int. Congr. Ser., v. 1263, p.754–757, 2004.MAES, L.; HAESEBROUCK, F.; PENSAERT, M. Experimental reproductionof clinical disease by intratracheal inoculation of fattening pigs withswine influenza virus isolates. Proc. Int. Congr. Pig Vet. Soc., v. 8, p. 60, 1984.MANCINI, D. A. P.; CUNHA, E. M. S.; MENDONÇA, R. M. Z. Evidenceof swine respiratory infection by influenza viruses in Brazil. VirusRev. Res., v. 11, p. 39-43, 2006.MATROSOVICH, M. N.; MATROSOVICH, T. Y.; GRAY, T. et al. Neuraminidaseis important for the initiation of influenza virus infection inhuman airway epithelium. J. Virol., v. 78, p. 12665-12667, 2004.MYERS, K. P.; OLSEN, C. W.; GRAY, G. C. Cases of Swine Influenza in Humans:A Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis., v.44, p. 1084–1088, 2007.NEWMAN, A.P.; REISDORF, E.; BEINEMANN, J. et al. Human case ofswine influenza A (H1N1) triple reassortant virus infection, Wisconsin.Emerging Infect. Dis., v. 14, p. 1470-1472, 2008.NICHOLLS, J. M.; CHAN, M. C. W.; CHAN, W. Y. et al. Tropism ofavian influenza A (H5N1) in the upper and lower respiratory tract. Nat.Med., v. 13, p. 147-149,2007.OLSEN, C. W.; CAREY, S.; HINSHAW, L. et al. Virologic and serologicsurveillance for human, swine and avian influenza virus infections among pigsin the north-central United States. Arch. Virol., v. 145, p. 1399–1419, 2000.OLSEN, C.W.; BROWN, I.H.; EASTER<strong>DA</strong>Y, B. C.; VAN REETH, K.Swine influenza. In: STRAW, B. E.; ZIMMERMAN, J.J.; D’ALLAIRE,S.; TAYLOR, D. J. (Ed). Diseases of swine. 9th ed. Ames: Iowa State UniversityPress, 2006. p. 469-482.PALESE, P.; SHAW, M. L. Orthomyxoviridae: The viruses and theirreplication. In: KNIPE, D. M.; HOWLEY, P. M.; GRIFFIN, D. E.; LAMB,R. A.; MARTIN, M. A.; ROIZMAN, B.; STRAUS, S. E. (Ed.). Fields Virology.5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007. p. 1647–1689.PASMA. T.; JOSEPH. T. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 infection in swineherds, Manitoba, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis., v. 16, p. 706-708, 2010.PERE<strong>DA</strong>, A.; CAPPUCCIO, J.; QUIROGA, M.A. et al. Pandemic(H1N1) 2009 outbreak on a pig farm, Argentina. Emerg. Infect. Dis.,v.16, p.304-307, 2010.PIÑEYRO, P.E.; CAPUCCIO, J.A.; MACHUCA, M.A. et al. Seroprevalenceof swine influenza virus in fattener pigs in Argentina, evaluated byinhibition of hemagglutination (HI) test and ELISA test. In: INTERNA-TIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON EMERGING AND RE-EMERGING PIGDISEASES, 5., 2007, Krakow. Proceedings... Pulawy: National VeterinaryResearch Institute, 2007.RICHT, J. A.; LAGER, K. M.; JANKE, B. H. et al. Pathogenic and antigenicproperties of phylogenetically distinct reassortant H3N2 swine influenzaviruses cocirculating in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol., v.41, p. 3198-3205, 2003.SCHAEFER, R.; TREVISOL, I. M.; PALUDO, E. Avaliação da presençado vírus influenza em suínos no sul do Brasil. In: BOLETIM DEPESQUISA E DESENVOLVIMENTO, 10. 2008, Concórdia. Boletim dePesquisa e Desenvolvimento... Concórdia: Embrapa Suínos e Aves 2008. 18 p.SHINYA, S.; EBINALL, M.; YAMA<strong>DA</strong>, S. et al. Influenza virus receptorsin the human airway. Nature, v.440, p.435-436, 2006.SMITH, G. J. D.; VIJAYKRISHNA, D.; BAHL, J. et al. Origins and evolutionarygenomics of the 2009 swine-origin H1N1 influenza A epidemic.Nature, v. 459, 2009.SRETA, D.; TANTAWET, S.; AYUDHYA, S. N. N. et al. Pandemic(H1N1) 2009 Virus on Commercial Swine Farm, Thailand. . Emerg. Infect.Dis., v. 16, p. 1587-1590, 2010.THACKER, E. L.; THACKER, B. J.; JANKE, B. H. Interaction betweenMycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Swine Influenza Virus. J. Clin. Microbiol.,v. 39, p. 2525–2530, 2001.THACKER, E.; JANKE, B. Swine influenza virus: zoonotic potential andvaccination strategies for the control of avian and swine influenzas. J. Infect.Dis., v. 197, Suppl 1, p. 19-24, 2008.VAN REETH, K. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of influenza. Vet. Microbiol.,v.74, p. 109-116, 2000.VAN REETH, K.; BROWN, I. H.; DURRWALD, R. et al. Seroprevalenceof H1N1, H3N2 and H1N2 influenza viruses in pigs in seven Europeancountries in 2002–2003. Influenza Other Respi. Viruses, 2, 99–105, 2008.VANNIER, P. Infectious causes of abortion in swine. Reprod. Dom.Anim., v. 34, p.367–376, 1999.VINCENT, L. L.; JANKE, B. H.; PAUL, P. S.; HALBUR, P. G. A monoclonal-antibody-basedimmunohistochemical method for the detection ofswine influenza virus in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J.Vet. Diagn. Invest., v. 9, p.191-195, 1997.VINCENT, A. L.; LAGER, K. M.; HARLAND, M. et al. Absence of 2009Pandemic H1N1 Influenza A Virus in Fresh Pork. PLoS ONE., v. 4,doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008367. 2009.WEBSTER, R. G.; LAVER, W. G.; AIR, G. M. et al. Molecular mechanismsof variation in influenza viruses. Nature, v. 296, p. 115-121, 1982.WESLEY, R. D. Exposure of sero-positive gilts to swine influenza virus maycause a few stillbirths per litter. Can. J. Vet. Res., v. 68, p.215–217, 2004.WRIGHT, P. F.; NEUMANN, G.; KAWAOKA, Y. Orthomyxoviruses. In:KNIPE, D. M.; HOWLEY, P. M.; GRIFFIN, D. E.; LAMB, R. A.; MAR-TIN, M. A.; ROIZMAN, B.; STRAUS, S. E. (Ed.). Fields Virology. 5thed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007. p. 1691–1740.ZHOU, N. N.; SENNE, D. A.; LANDGRAF, J. S. et al. Genetic reassortmentof avian, swine, and human influenza A viruses in American pigs.J. Virol., v. 73, p. 8851–8856, 1999.Figura 1 - Hepatização crânio ventral compatírvel com infecçãopelo vírus da influenza ou Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Figura 2 - Hiperplasia de epitélio bronquiolar, secundário a infecção,pelo vírus da infecção da influenza.46 V&Z EM MINAS