01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
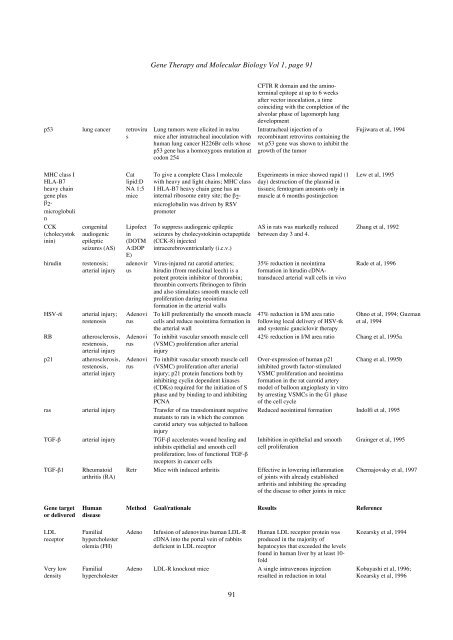
p53 lung cancer retroviru<br />
s<br />
MHC class I<br />
HLA-B7<br />
heavy chain<br />
gene plus<br />
β2microglobuli<br />
n<br />
CCK<br />
(cholecystok<br />
inin)<br />
congenital<br />
audiogenic<br />
epileptic<br />
seizures (AS)<br />
hirudin restenosis;<br />
arterial injury<br />
HSV-tk arterial injury;<br />
restenosis<br />
RB atherosclerosis,<br />
restenosis,<br />
arterial injury<br />
p21 atherosclerosis,<br />
restenosis,<br />
arterial injury<br />
Cat<br />
lipid:D<br />
NA 1:5<br />
mice<br />
Lipofect<br />
in<br />
(DOTM<br />
A:DOP<br />
E)<br />
adenovir<br />
us<br />
Adenovi<br />
rus<br />
Adenovi<br />
rus<br />
Adenovi<br />
rus<br />
<strong>Gene</strong> Therapy and <strong>Molecular</strong> <strong>Biology</strong> Vol 1, page 91<br />
Lung tumors were elicited in nu/nu<br />
mice after intratracheal inoculation with<br />
human lung cancer H226Br cells whose<br />
p53 gene has a homozygous mutation at<br />
codon 254<br />
To give a complete Class I molecule<br />
with heavy and light chains; MHC class<br />
I HLA-B7 heavy chain gene has an<br />
internal ribosome entry site; the β2microglobulin<br />
was driven by RSV<br />
promoter<br />
To suppress audiogenic epileptic<br />
seizures by cholecystokinin octapeptide<br />
(CCK-8) injected<br />
intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.)<br />
Virus-injured rat carotid arteries;<br />
hirudin (from medicinal leech) is a<br />
potent protein inhibitor of thrombin;<br />
thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin<br />
and also stimulates smooth muscle cell<br />
proliferation during neointima<br />
formation in the arterial walls<br />
To kill preferentially the smooth muscle<br />
cells and reduce neointima formation in<br />
the arterial wall<br />
To inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell<br />
(VSMC) proliferation after arterial<br />
injury<br />
To inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell<br />
(VSMC) proliferation after arterial<br />
injury; p21 protein functions both by<br />
inhibiting cyclin dependent kinases<br />
(CDKs) required for the initiation of S<br />
phase and by binding to and inhibiting<br />
PCNA<br />
ras arterial injury Transfer of ras transdominant negative<br />
mutants to rats in which the common<br />
carotid artery was subjected to balloon<br />
injury<br />
TGF-β arterial injury TGF-β accelerates wound healing and<br />
inhibits epithelial and smooth cell<br />
proliferation; loss of functional TGF-β<br />
receptors in cancer cells<br />
TGF-β1 Rheumatoid<br />
arthritis (RA)<br />
<strong>Gene</strong> target<br />
or delivered<br />
LDL<br />
receptor<br />
Very low<br />
density<br />
Human<br />
disease<br />
Familial<br />
hypercholester<br />
olemia (FH)<br />
Familial<br />
hypercholester<br />
91<br />
CFTR R domain and the aminoterminal<br />
epitope at up to 6 weeks<br />
after vector inoculation, a time<br />
coinciding with the completion of the<br />
alveolar phase of lagomorph lung<br />
development<br />
Intratracheal injection of a<br />
recombinant retrovirus containing the<br />
wt p53 gene was shown to inhibit the<br />
growth of the tumor<br />
Experiments in mice showed rapid (1<br />
day) destruction of the plasmid in<br />
tissues; femtogram amounts only in<br />
muscle at 6 months postinjection<br />
AS in rats was markedly reduced<br />
between day 3 and 4.<br />
35% reduction in neointima<br />
formation in hirudin cDNAtransduced<br />
arterial wall cells in vivo<br />
47% reduction in I/M area ratio<br />
following local delivery of HSV-tk<br />
and systemic ganciclovir <strong>therapy</strong><br />
Fujiwara et al, 1994<br />
Lew et al, 1995<br />
Zhang et al, 1992<br />
Rade et al, 1996<br />
Ohno et al, 1994; Guzman<br />
et al, 1994<br />
42% reduction in I/M area ratio Chang et al, 1995a<br />
Over-expression of human p21 Chang et al, 1995b<br />
inhibited growth factor-stimulated<br />
VSMC proliferation and neointima<br />
formation in the rat carotid artery<br />
model of balloon angioplasty in vitro<br />
by arresting VSMCs in the G1 phase<br />
of the cell cycle<br />
Reduced neointimal formation Indolfi et al, 1995<br />
Inhibition in epithelial and smooth<br />
cell proliferation<br />
Retr Mice with induced arthritis Effective in lowering inflammation<br />
of joints with already established<br />
arthritis and inhibiting the spreading<br />
of the disease to other joints in mice<br />
Grainger et al, 1995<br />
Method Goal/rationale Results Reference<br />
Adeno Infusion of adenovirus human LDL-R<br />
cDNA into the portal vein of rabbits<br />
deficient in LDL receptor<br />
Human LDL receptor protein was<br />
produced in the majority of<br />
hepatocytes that exceeded the levels<br />
found in human liver by at least 10fold<br />
Adeno LDL-R knockout mice A single intravenous injection<br />
resulted in reduction in total<br />
Chernajovsky et al, 1997<br />
Kozarsky et al, 1994<br />
Kobayashi et al, 1996;<br />
Kozarsky et al, 1996