01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
01. Gene therapy Boulikas.pdf - Gene therapy & Molecular Biology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
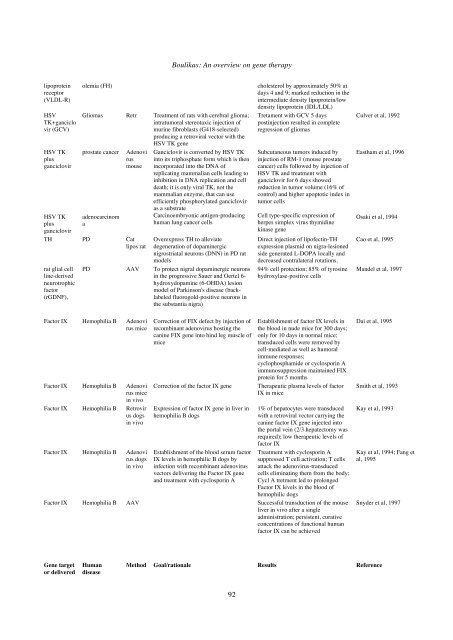
lipoprotein<br />
receptor<br />
(VLDL-R)<br />
HSV<br />
TK+ganciclo<br />
vir (GCV)<br />
HSV TK<br />
plus<br />
ganciclovir<br />
HSV TK<br />
plus<br />
ganciclovir<br />
<strong>Boulikas</strong>: An overview on gene <strong>therapy</strong><br />
olemia (FH) cholesterol by approximately 50% at<br />
days 4 and 9; marked reduction in the<br />
intermediate density lipoprotein/low<br />
density lipoprotein (IDL/LDL)<br />
Gliomas Retr Treatment of rats with cerebral glioma;<br />
intratumoral stereotaxic injection of<br />
murine fibroblasts (G418-selected)<br />
producing a retroviral vector with the<br />
HSV TK gene<br />
prostate cancer Adenovi<br />
rus<br />
mouse<br />
adenocarcinom<br />
a<br />
TH PD Cat<br />
lipos rat<br />
rat glial cell<br />
line-derived<br />
neurotrophic<br />
factor<br />
(rGDNF),<br />
Ganciclovir is converted by HSV TK<br />
into its triphosphate form which is then<br />
incorporated into the DNA of<br />
replicating mammalian cells leading to<br />
inhibition in DNA replication and cell<br />
death; it is only viral TK, not the<br />
mammalian enzyme, that can use<br />
efficiently phosphorylated ganciclovir<br />
as a substrate<br />
Carcinoembryonic antigen-producing<br />
human lung cancer cells<br />
Overexpress TH to alleviate<br />
degeneration of dopaminergic<br />
nigrostriatal neurons (DNN) in PD rat<br />
models<br />
PD AAV To protect nigral dopaminergic neurons<br />
in the progressive Sauer and Oertel 6hydroxydopamine<br />
(6-OHDA) lesion<br />
model of Parkinson's disease (backlabeled<br />
fluorogold-positive neurons in<br />
the substantia nigra)<br />
Factor IX Hemophilia B Adenovi<br />
rus mice<br />
Factor IX Hemophilia B Adenovi<br />
rus mice<br />
in vivo<br />
Factor IX Hemophilia B Retrovir<br />
us dogs<br />
in vivo<br />
Factor IX Hemophilia B Adenovi<br />
rus dogs<br />
in vivo<br />
Correction of FIX defect by injection of<br />
recombinant adenovirus hosting the<br />
canine FIX gene into hind leg muscle of<br />
mice<br />
92<br />
Tretament with GCV 5 days<br />
postinjection resulted in complete<br />
regression of gliomas<br />
Subcutaneous tumors induced by<br />
injection of RM-1 (mouse prostate<br />
cancer) cells followed by injection of<br />
HSV TK and treatment with<br />
ganciclovir for 6 days showed<br />
reduction in tumor volume (16% of<br />
control) and higher apoptotic index in<br />
tumor cells<br />
Cell type-specific expression of<br />
herpes simplex virus thymidine<br />
kinase gene<br />
Direct injection of lipofectin-TH<br />
expression plasmid on nigra-lesioned<br />
side generated L-DOPA locally and<br />
decreased contralateral rotations.<br />
94% cell protection; 85% of tyrosine<br />
hydroxylase-positive cells<br />
Establishment of factor IX levels in<br />
the blood in nude mice for 300 days;<br />
only for 10 days in normal mice;<br />
transduced cells were removed by<br />
cell-mediated as well as humoral<br />
immune responses;<br />
cyclophosphamide or cyclosporin A<br />
immunosuppression maintained FIX<br />
protein for 5 months<br />
Correction of the factor IX gene Therapeutic plasma levels of factor<br />
IX in mice<br />
Expression of factor IX gene in liver in<br />
hemophilia B dogs<br />
Establishment of the blood serum factor<br />
IX levels in hemophilic B dogs by<br />
infection with recombinant adenovirus<br />
vectors delivering the Factor IX gene<br />
and treatment with cyclosporin A<br />
1% of hepatocytes were transduced<br />
with a retroviral vector carrying the<br />
canine factor IX gene injected into<br />
the portal vein (2/3 hepatectomy was<br />
required); low therapeutic levels of<br />
factor IX<br />
Treatment with cyclosporin A<br />
suppressed T cell activation; T cells<br />
attack the adenovirus-transduced<br />
cells eliminating them from the body;<br />
Cycl A tretment led to prolonged<br />
Factor IX levels in the blood of<br />
hemophilic dogs<br />
Factor IX Hemophilia B AAV Successful transduction of the mouse<br />
liver in vivo after a single<br />
administration; persistent, curative<br />
concentrations of functional human<br />
factor IX can be achieved<br />
<strong>Gene</strong> target<br />
or delivered<br />
Human<br />
disease<br />
Culver et al, 1992<br />
Eastham et al, 1996<br />
Osaki et al, 1994<br />
Cao et al, 1995<br />
Mandel et al, 1997<br />
Dai et al, 1995<br />
Smith et al, 1993<br />
Kay et al, 1993<br />
Kay et al, 1994; Fang et<br />
al, 1995<br />
Snyder et al, 1997<br />
Method Goal/rationale Results Reference