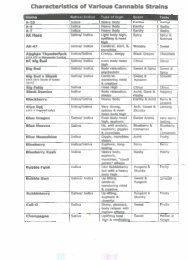
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Role of the endocannabinoid system in learning and memory 131<br />
by WIN-55212 or amphetamine was blocked by AM-251, and the amphetamine-induced<br />
LTD was facilitated by AM-404 [163]. Additionally, LTD in the<br />
neocortex [164] as well as in the nucleus accumbens [165, 166] has been<br />
shown to be dependent on presynaptic activation of CB 1 receptors.<br />
Interestingly, chronic exposure to ∆ 9 -THC or WIN-552-2 has been shown to<br />
prevent the induction of LTD, suggesting a functional tolerance that may partially<br />
underlie putative, long-lasting cognitive deficits associated with chronic<br />
marijuana use [166].<br />
This hypothesized role of endocannabinoids as initiators/mediators of LTD<br />
is also consistent with a series of experiments examining the effects of<br />
cannabinoid agonists and CB 1 antagonists on synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal<br />
cortex [167]. Tetanic stimulation induced plasticity in slightly more<br />
than half of the neurons examined, with approximately equal numbers of cells<br />
developing LTP and LTD. However, in the presence of WIN-55212-2 almost<br />
all of the plastic synapses showed LTD, while in the presence of SR-141716<br />
almost all of the plastic synapses developed LTP. The consequences of such a<br />
shift on learning are unclear, though it may suggest that forms of learning<br />
heavily dependent on LTP could be attenuated by endocannabinoids, while<br />
forms of learning heavily dependent on LTD could actually be enhanced.<br />
Other forms of synaptic plasticity<br />
Endocannabinoids have also been shown to modify other forms of synaptic<br />
plasticity. For example, anandamide has been shown to inhibit an interesting<br />
though poorly understood phenomena referred to as long-term transformation<br />
(LTT), where GABAergic inhibition is “transformed” into excitation when<br />
presynaptic tetanic stimulation is paired with postsynaptic depolarization<br />
[168]. This LTT has been shown to play an important role in pairing-induced<br />
LTP, which is also inhibited by anandamide [168].<br />
In addition to changes in presynaptic transmitter release and postsynaptic<br />
sensitivity, synaptic plasticity can be supported by the growth of new synapses,<br />
a process that has also been shown to be sensitive to CB 1 stimulation.<br />
Anandamide, ∆ 9 -THC, and WIN-55212-2 have all been shown to inhibit new<br />
synapse formation induced by forskolin, probably due to CB 1 receptor-mediated<br />
decreases in cAMP [169].<br />
Conclusions on the effects of endocannabinoids on cognition<br />
The weight of evidence clearly demonstrates that the endocannabinoid system<br />
is critically involved with physiological mechanisms underling learning and<br />
memory. It can be stated with a high degree of confidence that CB 1 receptors<br />
located in brain areas associated with learning and memory, including the hippocampus,<br />
frontal cortex, and striatum, are a crucial element of this influence.