- Page 2:
(( 3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 ))
- Page 6:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 10:
Contents List of contributors . . .
- Page 14:
List of contributors Itai A. Bab, B
- Page 18:
Preface Twenty years ago the endoca
- Page 22:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 26:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 30:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 34:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 38:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 42:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 46:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 50:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 54:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 58:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 62:
Cannabis in India: ancient lore and
- Page 66:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 70:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 74:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 78:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 82:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 86:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 90:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 94:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 98:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 102:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 106:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 110:
Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview
- Page 114:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 118:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 122:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 126:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 130:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 134:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 138:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 142:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 146:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 150:
Cannabidiol as a potential medicine
- Page 154:
68 M. Maccarrone it appears to acce
- Page 158:
70 M. Maccarrone Figure 1. Local ef
- Page 162:
72 M. Maccarrone FAAH and human rep
- Page 166:
74 M. Maccarrone FAAH and the regul
- Page 170:
76 M. Maccarrone avenue to the deve
- Page 174:
78 M. Maccarrone 41 Maccarrone M, C
- Page 178:
80 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. other
- Page 182:
82 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. anti-g
- Page 186:
84 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. exerte
- Page 190:
86 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. glial
- Page 194:
88 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. in par
- Page 198:
90 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. 2-AG w
- Page 202:
92 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. rats w
- Page 206:
94 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. same s
- Page 210:
96 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. Cannab
- Page 214:
98 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. tory p
- Page 218:
100 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. the p
- Page 222:
102 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. (2001
- Page 226:
104 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. 61 Ad
- Page 230:
106 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. fonyl
- Page 234:
108 J. Fernández-Ruiz et al. 154 V
- Page 238:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 242:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 246:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 250:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 254:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 258:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 262:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 266:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 270:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 274:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 278:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 282:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 286:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 290:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 294:
Role of the endocannabinoid system
- Page 298:
Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 302:
Cannabinoids and anxiety 143 CB 1 r
- Page 306:
Cannabinoids and anxiety 145 Crippa
- Page 310:
Cannabinoids and anxiety 147 effect
- Page 314:
150 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker the
- Page 318:
152 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker into
- Page 322:
154 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker Stud
- Page 326:
156 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker perh
- Page 330:
158 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker dose
- Page 334:
160 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker 30 N
- Page 338:
162 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker 76 M
- Page 342:
164 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker 120
- Page 346:
166 L. De Petrocellis et al. such a
- Page 350:
168 L. De Petrocellis et al. Figure
- Page 354:
170 L. De Petrocellis et al. ro-ana
- Page 358:
172 L. De Petrocellis et al. a poss
- Page 362: 174 L. De Petrocellis et al. human
- Page 366: 176 L. De Petrocellis et al. phine
- Page 370: 178 L. De Petrocellis et al. factor
- Page 374: 180 L. De Petrocellis et al. diatio
- Page 378: Cannabinoids as Therapeutics Edited
- Page 382: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 386: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 390: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 394: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 398: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 402: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 406: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 410: Cannabinoids: effects on vomiting a
- Page 416: 202 I.A. Bab signaling [20, 21] as
- Page 420: 204 I.A. Bab cular and cellular bio
- Page 424: 206 I.A. Bab 39 Iuliano-Burns S, Mi
- Page 428: 208 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino (Amer
- Page 432: 210 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino addic
- Page 436: 212 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino Condi
- Page 440: 214 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino plete
- Page 444: 216 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino prote
- Page 448: 218 D. Parolaro and T. Rubino Exp T
- Page 452: 220 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 456: 222 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 460: 224 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 464:
226 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 468:
228 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 472:
230 F. Barth and M. Rinaldi-Carmona
- Page 476:
232 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott However
- Page 480:
234 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott In the
- Page 484:
236 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott ∆ 9 -
- Page 488:
238 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Figure
- Page 492:
240 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott For the
- Page 496:
242 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Figure
- Page 500:
244 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott oxide,
- Page 504:
246 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Ireland
- Page 508:
248 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Figure
- Page 512:
250 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Figure
- Page 516:
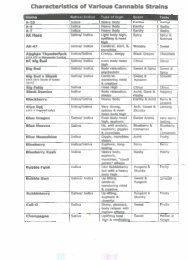
252 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Table 2
- Page 520:
254 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott of the
- Page 524:
256 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott reactio
- Page 528:
258 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott Figure
- Page 532:
260 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott easily
- Page 536:
262 G.W. Guy and C.G. Stott 40 Walt
- Page 540:
Index AA-5-HT 156 absent-mindedness
- Page 544:
Index 267 cannabinoid agonist 190,
- Page 548:
Index 269 HU-210 93, 95, 142, 153,
- Page 552:
Index 271 oxidative cell death 84 o