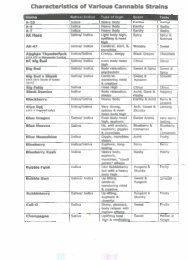
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
3. Umbruch 4.4..2005 - Online Pot
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
152 S.M. Huang and J.M. Walker<br />
into the systemic circulation. This finding indicates that CB 1R agonists acting<br />
in the periphery are sufficient to inhibit pain. Intraplantar administration of the<br />
mixed CB 1/CB 2 agonist WIN-55,212-2 also attenuated the development of carrageenan-evoked<br />
mechanical hyperalgesia, allodynia and spinal Fos protein<br />
expression in a CB 1R- and CB 2R-dependent manner [30].<br />
Effects of cannabinoid CB 2-specific agonists<br />
CB 2Rs are either absent or expressed in low levels by neural tissues [7, 46] but<br />
are present on immune cells and hence may have implications for pain. This<br />
distribution has led to the evaluation and validation of the CB 2R as a target for<br />
novel pharmacotherapies for pain, an attractive possibility because CB 2R agonists<br />
lack psychotropic side effects.<br />
CB 2R agonists are anti-nociceptive in models of acute [47] and persistent<br />
[29, 48–51] pain. Hanusˇ and colleagues [49] demonstrated that the selective<br />
CB 2 agonist HU-308 produced marked decreases in pain behavior in rats<br />
receiving hindpaw injections of dilute formalin with no change in motor function,<br />
a side effect often seen with CB 1R agonists which may predict psychoactivity<br />
in humans. Another CB 2R agonist, AM-1241, has also been shown<br />
to induce CB 2R-mediated analgesia in acute pain paradigms while failing to<br />
elicit centrally mediated side effects such as hypothermia, catalepsy and<br />
hypoactivity [47]. In inflammatory pain models, AM-1241 also induces<br />
CB 2R-mediated suppression of carrageenan- and capsaicin-evoked thermal<br />
and mechanical hyperalgesia and allodynia [30, 50, 52].<br />
Substances released by immune cells such as histamine, serotonin<br />
(5-hydroxytryptamine), eicosanoids, interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor-α,<br />
and nerve growth factor sensitize nociceptors [53–55]. Therefore, it is plausible<br />
that activation of CB 2Rs on immune cells could suppress pain.<br />
Cannabinoid agonists have been shown to inhibit the release of inflammatory<br />
mediators from monocytic cells [56] and mast cells [57]. Direct effects on<br />
CB 2Rs localized to primary afferents have been postulated [58–62], though the<br />
basis for such effects is unclear in light of the paucity or lack of CB 2R expression<br />
in neural tissues. It would appear from these findings that CB 2R selective<br />
agonists are a promising target for drugs to treat pain and inflammation.<br />
Effects of cannabinoid agonists in humans<br />
The human trials of cannabis and ∆ 9 -THC are few in number and typically<br />
small in subject size. There are marked differences between studies in dose<br />
regimens and drug preparations, with some using smoked marijuana and others<br />
using ∆ 9 -THC by oral or intravenous routes. Some studies used healthy<br />
volunteers, whereas others used patients with clinical pain. Therefore, it is<br />
important to note that: (1) some negative results may have arisen from admin-